Collectors
Supported options
The administration view now allows users to use the Preview feature to see the result of the configuration without the items being processed further for the Assess view. This feature is available for RSS, Simple Web and RT collector.
RSS Collector
RSS Collector enables Taranis AI to collect data from a user-defined RSS feed (See RSS feeds details).
- Required fields:
- FEED_URL
- Optional fields:
- USER_AGENT
- PROXY_SERVER
- USE_GLOBAL_PROXY (ignore anything set in the
PROXY_SERVERfield, use what is currently set as a default in Settings; learn more in section Settings) - ADDITIONAL_HEADERS [accepts a valid
json] (can be used to add additional headers, not all headers work as expected) - CONTENT_LOCATION (use
keyof the feed schema, from where the content for news items should be extracted (e.g.descriptionof the feed entry); if thekeyfor a feed entry is not found, it falls back to behaviour, as if the key was not entered at all) - XPATH (set this to specify the location of scraped element on the website, where the RSS feed entry points to; this is not an XPATH inside the RSS Feed)
- TLP_LEVEL
- REFRESH_INTERVAL (see Bots - refresh_interval)
- DIGEST_SPLITTING On/Off (creates News Items out of URLs present in the
Summaryfield of RSS feed) - DIGEST_SPLITTING_LIMIT (default: 30)
- BROWSER_MODE On/Off (see Browser Mode)
Basic configuration
- Example:
- FEED_URL: https://www.bmi.gv.at/rss/bmi_presse.xml
Advanced configuration
The RSS Collector supports the use of XPath for locating elements. (See Simple Web Collector Advanced configuration)
- Example:
- FEED_URL: https://www.bmi.gv.at/rss/bmi_presse.xml
- XPATH: //*[@id=“getting-started-web-console-creating-new-project_openshift-web-console”]
- ADDITIONAL_HEADERS:
{ "AUTHORIZATION": "Bearer Token1234", "X-API-KEY": "12345", "Cookie": "firstcookie=1234; second-cookie=4321", }
Simple Web Collector
Simple Web Collector enables Taranis AI to collect data using web URLs and XPaths.
- Required field:
- WEB_URL
- Optional fields:
- USER_AGENT
- PROXY_SERVER
- USE_GLOBAL_PROXY
- ADDITIONAL_HEADERS
- XPATH (set to specify the location of the scraped element on the website)
- TLP_LEVEL
- DIGEST_SPLITTING On/Off
- DIGEST_SPLITTING_LIMIT (default: 30)
- BROWSER_MODE On/Off (see Browser Mode)
Basic configuration
The simplest way to use this collector is to use the WEB_URL field only. By using only the WEB_URL field, Taranis-AI autonomously determines the content to be collected. Even though it is mostly reliable, sometimes it is not perfect.
Advanced configuration
When content cannot be reliably collected using the Basic configuration, adding the attribute XPATH (See tutorial how to find it), can be useful. It is crucial to specify the XPath of the precise element containing the desired data.
Configuration for Mastodon Feeds
To set up an RSS Collector for collecting posts from a Mastodon hashtag or user, follow these steps:
Finding the Mastodon RSS Feed URL:
- Hashtag Feed: Add
.rssto the hashtag URL. For example, to collect posts tagged with #cybersecurity:https://mastodon.social/tags/cybersecurity.rss - User Feed: Similarly, add
.rssto the user’s profile URL. Example:https://mastodon.social/@username.rss
- Hashtag Feed: Add
Creating a New RSS Source with Required Parameters: When creating the new RSS source, configure it with the following parameters. Here’s an example of how to fill out the fields:
- FEED_URL: Enter the RSS feed URL for the Mastodon hashtag or user (e.g.,
https://mastodon.social/tags/cybersecurity.rss). - CONTENT_LOCATION Set this to
"summary"to specify the main content location within each RSS entry. - REFRESH_INTERVAL Set the refresh interval in crontab-like style, see Bots - refresh_interval.
- DIGEST_SPLITTING is set to
"false"since we’re not splitting entries into multiple items.
- FEED_URL: Enter the RSS feed URL for the Mastodon hashtag or user (e.g.,
Configuration for Darkweb Feeds
Extend your compose.yml with a tor service, e.g.
tor:
image: "docker.io/dperson/torproxy:latest"
deploy:
restart_policy:
condition: always
environment:
# LOCATION: "AT"
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "200k"
max-file: "10"
Read details about the used docker image here
The important setting is “PROXY_SERVER” in the OSINT Source you want to crawl.
RT Collector
RT Collector enables Taranis AI to collect data from a user-defined Request Tracker instance.
RT Collector collects tickets, translates all ticket attachments into individual News Items. A ticket is represented via a Story. It also collects ticket Custom Fields and saves it as key-value pairs represented with Story attributes, visible whilst Story editing. On each collector execution an update to existing Stories occurs, so editing the Story values in Taranis AI is not recommended and handling it more like read-only items is better.
Required fields:
- BASE_URL: Base URL of the RT instance (e.g.
http://localhost). - RT_TOKEN: User token for the RT instance.
- BASE_URL: Base URL of the RT instance (e.g.
Optional fields:
- SEARCH_QUERY: query to use for filtering tickets (e.g. owner=‘user1’). It is possible to check this manually by: http://<rt_address>/REST/2.0/tickets?query=owner=‘user1’
- FIELDS_TO_INCLUDE: case-sensitive, comma-separated values; example: Email, IP; if not set, all ticket custom fields are ingested
- ADDITIONAL_HEADERS
- TLP_LEVEL
- USER_AGENT
- PROXY_SERVER
- USE_GLOBAL_PROXY
MISP Collector
Until the definitions of our MISP Objects are not officially part of the MISP platform, feel free to import them manually (see MISP Objects). This allows to edit the information of News Items and Story data directly in the MISP instance without Taranis AI.
MISP Collector enables Taranis AI to collect MISP events.
Required fields:
- URL: Base URL to the MISP instance (e.g.
https://localhost) - API_KEY: API key to access the instance (see MISP Automation API)
- URL: Base URL to the MISP instance (e.g.
Optional fields:
- SSL_CHECK: if enabled, the SSL certificate will be validated
- SHARING_GROUP_ID: set to the ID of a sharing group, if only one sharing group should be collected (see Create and manage Sharing Groups).
- REQUEST_TIMEOUT
- USER_AGENT
- PROXY_SERVER
- USE_GLOBAL_PROXY
- ADDITIONAL_HEADERS
- REFRESH_INTERVAL
How MISP Collector works
Essentially it works exactly like other collectors with one exception: conflicts. Given the nature of the collaborative environment of MISP events (they can be changed in the MISP platform by the owning organisation and secondary organisations can submit change requests using the MISP proposals). Due to that, there will likely occur conflicts when attempting to update existing Stories that were, in the meantime, internally modified.
Generally, conflicts occur the moment, a Story is modified internally, and has not been pushed to MISP immediately. Therefore, it is recommended to always try to keep Stories in sync with the MISP events. To update them in MISP with the Story (see Connectors).
Conflict resolution
Conflicts can currently be resolved in the Connectors section accessible in the general and administration dashboard.
In the Conflict Resolution View it is possible to resolve given conflicts.
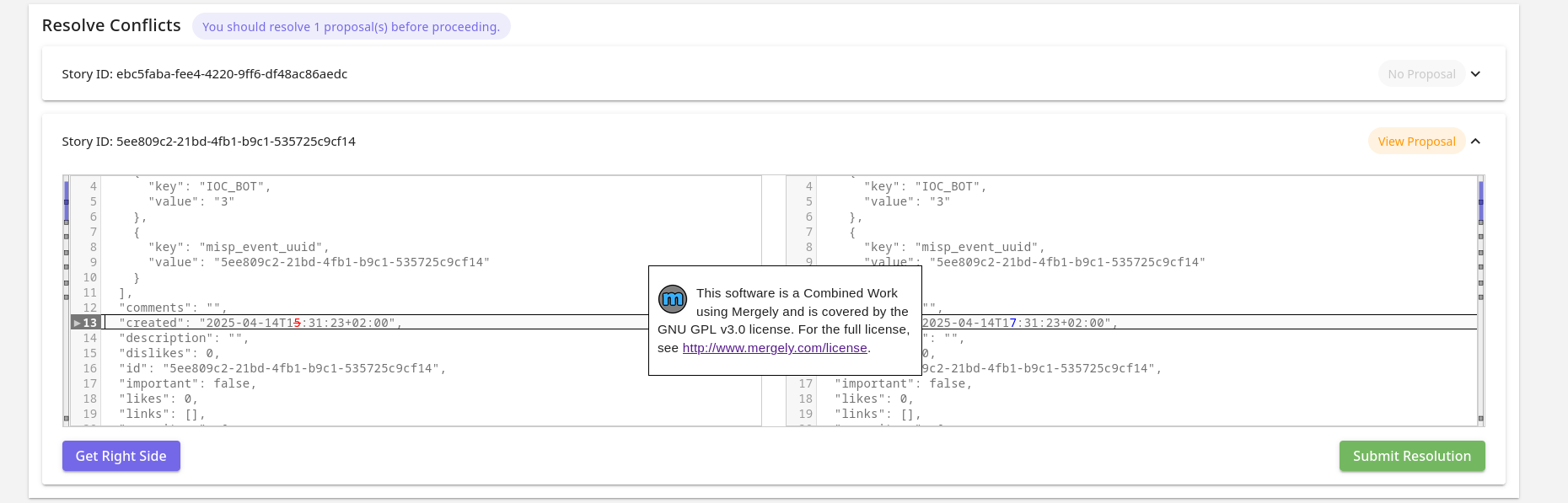
In the view, all stories that have conflicts will be shown in expandable cards. One by one it is possible to inspect them and resolve them.
At the top, the number of events (among the ones in conflict) have proposals to resolve is shown (only owned by your MISP organisation). It is recommended to resolve them first in MISP, before you resolve them in Taranis AI, so you work with the latest information. Once teh conflicts are resolved and changes are submitted, the Story will be updated without raising conflicts later on (until the Story gets modified internally). It is the users’ decision, whether they want to resolve the conflicts immediately with the version collected without proposals, or are skipped, preposals in MISP are resolved, and resolve conflicts later on next collection. In case a Story has proposals, it is possible to open the event in MISP with the “View Proposal” button.
The content on the left is the current Story. The content on the right hand side editor is the new content and is the content, which is the content that is used for the eventual update. It is possible to take the right or left side of each difference shown using the diff window by clicking the arrows on the left sides of each content window.
Both sides are freely editable and keyboard shortcuts for back and forward are supported. The context for keyboard shortcuts is decided based on where the cursor is (where it was clicked the last time - right or left side).
It is important, that the content on the right side stays a valid Story JSON.
With “Get Right Side” button, it is possible to check what content will be submitted. “Submit Resolution” button is used to submit the update.
Conflicts are stored in a temporary memory, to encourage a fresh MISP Collector recollection, before resolving conflicts and to prevent conflict resolution with outdated data.
Digest Splitting
Digest Splitting is a feature that allows the user to split all available URLs in the located element into individual News Items. The Digest Splitting Limit is the maximum number of URLs that will be split into individual News Items. If the limit is reached, the remaining URLs are dropped. The Digest Splitting Limit is set to 30 News Items by default but can be adjusted by the administrator. Useful in case of timeouts during collection of too many News Items.
Browser Mode
Collectors will fail if the web page content is only available with JavaScript. In that case it is possible to turn on the Browser Mode. All requests will have JavaScript enabled, therefore, it is slower and can use more resources.