Functionalities marked with 👤 are only accessible by admin users.
To print this documentation visit /_print/docs
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Functionalities marked with 👤 are only accessible by admin users.
To print this documentation visit /_print/docs
See docker/dev for instructions on how to start at dev setup.
Install from stable release
curl -fsSL https://taranis.ai/install.sh | bash
Clone via git
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/taranis-ai/taranis-ai
cd taranis-ai/docker/
Copy env.sample to .env
cp env.sample .env
Open file .env and change defaults if needed. More details about environment variables can be found in the README.md.
Taranis AI images are tagged as follows:
1.1.7)stable)latest)See Internal TLS Configuration for setting up TLS encryption and Advanced monitoring for more logging insights. For detailed information about container tags, release strategy, and deployment recommendations, see Releases and Container Tags.
See Advanced monitoring for more logging insights.
TO circumvent the potential reusage of older local images
docker compose pull
Start-up application
docker compose up -d
Use the application
http://<url>:<TARANIS_PORT>/login
The default credentials are user / user and admin / admin.
The passwords for these two default users can be overridden by setting the environment variables PRE_SEED_PASSWORD_ADMIN or PRE_SEED_PASSWORD_USER before first launch.
Afterwards they are stored in the database in the user table.
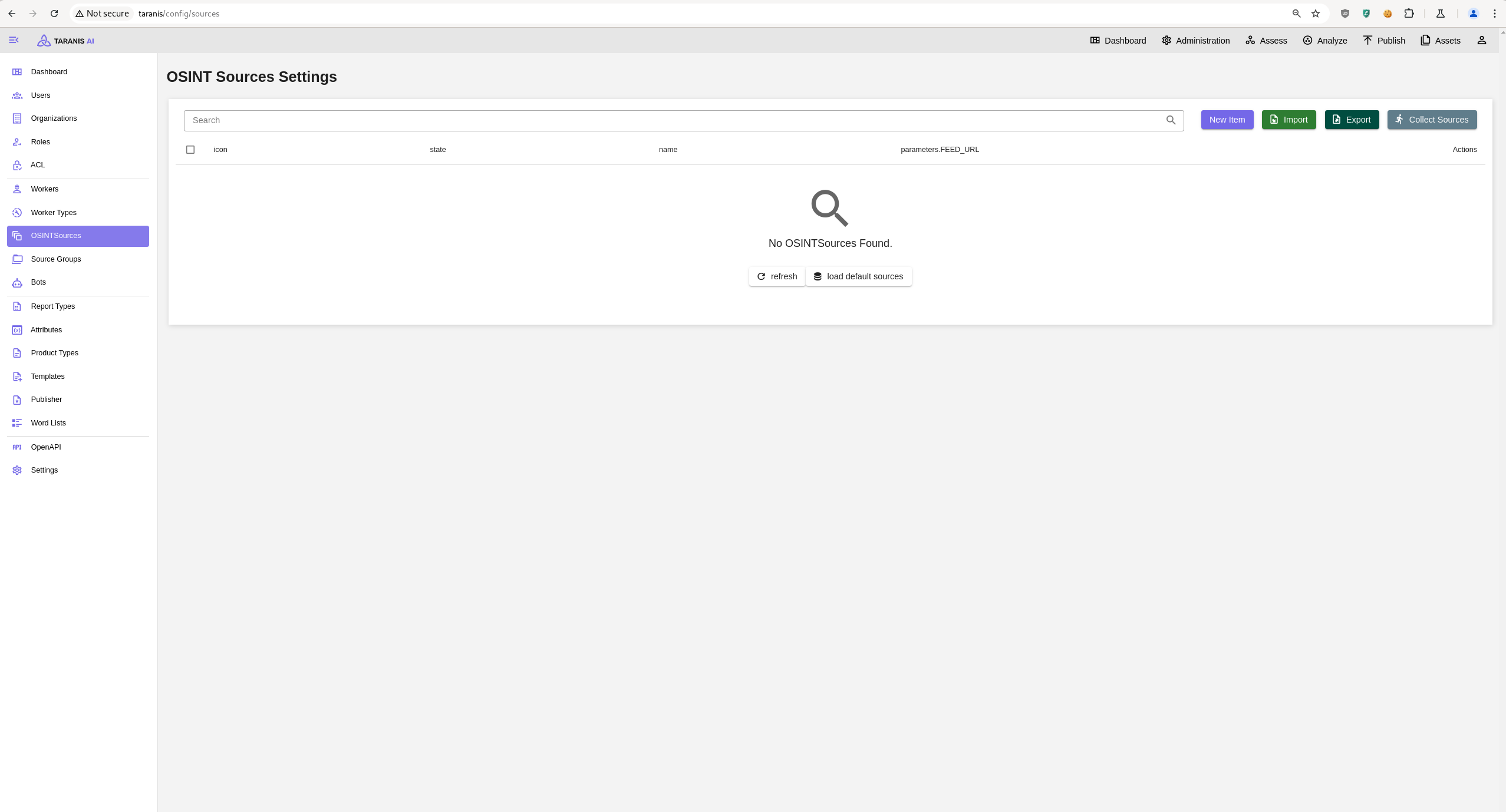
Open http://<url>:<TARANIS_PORT>/config/sources and click load default sources to import the default sources from: default_sources.json
Or import a source export via the Import.
Clone via git
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/taranis-ai/taranis-ai
cd taranis-ai/docker/
Copy env.sample to .env
cp env.sample .env
Open file .env and change defaults if needed. More details about environment variables can be found here.
See Internal TLS Configuration for setting up TLS encryption and Advanced monitoring for more logging insights. See Releases and Container Tags for information about container image versions, Internal TLS Configuration for setting up TLS encryption, and Advanced monitoring for more logging insights.
Download and install kompose.io
# resovle variables from .env into taranis-ai/docker/compose.yml
docker compose config > resolved-compose.yml
# convert compose file to kubernetes
kompose --file resolved-compose.yaml convert
If you want to connect to a kubernetes cluster you can do something like this:
kubectl create ns db
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm repo update
helm install pg-ha bitnami/postgresql-ha -n db \
--set postgresql.username=app \
--set postgresql.password=apppass \
--set postgresql.database=appdb \
--set pgpool.adminUsername=pgpool \
--set pgpool.adminPassword=pgpoolpass \
--set postgresql.replicaCount=2
kubectl -n db port-forward statefulset/pg-ha-postgresql 54321:5432 &
kubectl -n db port-forward pod/pg-ha-postgresql-1 54322:5432 &
And then connect with:
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI="postgresql+psycopg://app:apppass@/appdb?host=127.0.0.1,127.0.0.1&port=54321,54322&target_session_attrs=read-write&connect_timeout=3"
Taranis AI publishes container images to GitHub Container Registry (ghcr.io) with different tagging strategies for core services and bots.
All images are available at GitHub Container Registry.
Core Taranis AI services follow a stable and tested release process:
| Tag | Description | Use Case | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
stable | Latest manually tested and verified release | Production deployments | ✅ High |
v1.2.3 (semver) | Specific version (semantic versioning) | Pinned production deployments | ✅ High |
latest | Latest build from main branch | Development/testing only | ⚠️ May contain bugs |
Bot containers have a different tagging strategy focused on experimental features:
| Tag | Description | Use Case | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
latest (alias: stable) | Latest manually tested and verified release | Production bot deployments | ✅ High |
dev or experimental | Development builds with experimental features | Testing new bot capabilities | ⚠️ Experimental |
For the best experience using Taranis AI, we recommend that your system meet the following requirements:
| Resource | Minimal (w/o bots) | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 2 cores | 12 cores |
| RAM | 2 GB | 16 GB |
| Storage | 16 GB | 40 GB |
Note: The recommended requirements assume that all bots are active concurrently. You can estimate the requirements for running only some of the bots from this table:
| Bot | CPUs | RAM | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| cybersec-classifier | 2 | 2.0 GB | 8.3 GB |
| NER | 2 | 7.0 GB | 8.38 GB |
| story-clustering | 2 | 1.5 GB | 6.8 GB |
| summary | 2 | 1.5 GB | 8.4 GB |
| sentiment-analysis | 2 | 2.5 GB | 8.12 GB |
You can assume the number of CPUs and RAM to be cumulative, so for running two bots concurrently, sum up the required number of CPUs and RAM. Reserve an additional 2 CPUs and 2 GB RAM for normal system operation.
Example: For running story-clustering and NER bots at the same time, your system should have 6 CPUs and 10.5 GB of RAM.
GPU support for accelerating bot performance will be available soon. Further details and configuration options will be provided once this feature is launched.
Supported upgrade of PostgreSQL 14.x to PostgreSQL 17.x. This upgrade is capable of upgrading a fully running instance of Taranis AI. Expect Taranis AI downtime during the process of the upgrade.
docker/compose.yml file.docker/compose.yml) is setup to use the image of PostgreSQL 17 (check your POSTGRES_TAG variable in the .env file)taranis-ai/dockerupgrade-database.sh is executable./upgrade-database.shAll containers should now be again up and running!
SENTRY_DSN) ready.Sentry is a monitoring tool that enables more insights about an application. Taranis AI takes advantage of this if you enable it at the start up.
Sentry can be used to monitor insights about GUI, Core and database. In Taranis AI: Issues, Traces, Profiles and Queries can be tracked.
To enable Sentry, set the SENTRY_DSN variables in the .env file before start of the application. More details about environment variables can be found here.
To gain insights about GUI, use the TARANIS_GUI_SENTRY_DSN variable and set it to your Sentry DSN address.
To gain insights about Core and database, use the TARANIS_CORE_SENTRY_DSN variable and set it to your Sentry DSN address.
This guide explains how to configure TLS (Transport Layer Security) for Taranis AI using the Granian ASGI server. TLS provides encrypted communication between clients and the server, essential for secure deployments.
The primary TLS configuration is handled through Granian environment variables:
For a basic TLS setup, configure these environment variables:
# SSL Certificate file path
GRANIAN_SSL_CERTIFICATE=/path/to/your/certificate.pem
# SSL Private key file path
GRANIAN_SSL_KEYFILE=/path/to/your/private_key.pem
# Turn off verification of self-signed certificates in Frontend and Worker service
SSL_VERIFICATION=False
DISABLE_SSE=True
When enabling TLS, you must also update the core URL to use HTTPS:
# Update the core API URL to use HTTPS
TARANIS_CORE_URL=https://your-domain.com/api
This variable affects multiple components:
TARANIS_CORE_URL to communicate with the core APITARANIS_CORE_URL for API communication (falls back to http://{TARANIS_CORE_HOST}{TARANIS_BASE_PATH}api if not set)TARANIS_CORE_API in config.jsonMore Granian environmental variables that affect SSL are derived from the CLI options prefixed with --ssl-*.
Examples:
GRANIAN_SSL_KEYFILE_PASSWORD
GRANIAN_SSL_CA
GRANIAN_SSL_CRL
GRANIAN_SSL_CLIENT_VERIFY
Make sure, all variables are properly set in the compose file. The variable SSL_VERIFICATION can be set for the frontend and worker service.
./certs:/certs:ro)SSL_VERIFICATION=False)https:// prefix. Moreover, the Certificate Authority needs to be added into the container’s trust store by mounting it under /usr/local/share/… Read more at docker.com.Here’s an example Docker Compose configuration with TLS enabled:
services:
core:
image: ghcr.io/taranis-ai/taranis-core:latest
environment:
# TLS configuration (paths must match the mounted cert directory)
- GRANIAN_SSL_CERTIFICATE=/certs/certificate.pem
- GRANIAN_SSL_KEYFILE=/certs/private_key.pem
- TARANIS_CORE_URL=https://your-domain.com/api
- DB_URL=database
- DB_DATABASE=taranis
- DB_USER=taranis
- DB_PASSWORD=supersecret
- API_KEY=your-secure-api-key
- JWT_SECRET_KEY=your-secure-jwt-secret
volumes:
# Mount local certificate directory into the container
- ./certs:/certs:ro
- core_data:/app/data
depends_on:
- database
- rabbitmq
ports:
- "8443:8080"
networks:
- taranis_network
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "curl --fail https://localhost:8080/api/health || exit 1"]
interval: 90s
timeout: 30s
retries: 5
start_period: 40s
volumes:
core_data:
networks:
taranis_network:
driver: bridge
For Kubernetes deployments, configure TLS using ConfigMaps and Secrets:
# TLS Secret
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: taranis-tls
type: kubernetes.io/tls
data:
tls.crt: <base64-encoded-certificate>
tls.key: <base64-encoded-private-key>
---
# Core Deployment with TLS
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: taranis-core
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: taranis-core
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: taranis-core
spec:
containers:
- name: core
image: ghcr.io/taranis-ai/taranis-core:latest
env:
- name: GRANIAN_SSL_CERTIFICATE
value: "/certs/tls.crt"
- name: GRANIAN_SSL_KEYFILE
value: "/certs/tls.key"
- name: TARANIS_CORE_URL
value: "https://your-domain.com/api"
- name: API_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: taranis-secrets
key: api-key
- name: JWT_SECRET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: taranis-secrets
key: jwt-secret
volumeMounts:
- name: tls-certs
mountPath: /certs
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: tls-certs
secret:
secretName: taranis-tls
Corrensponds to Taranis release 1.2.4
Assess displays a list of collected news items from various sources, which can be searched, filtered, and sorted based on different attributes (see Filters). Furthermore, news items can be merged, added to reports, analyzed and have their state changed (see Items).
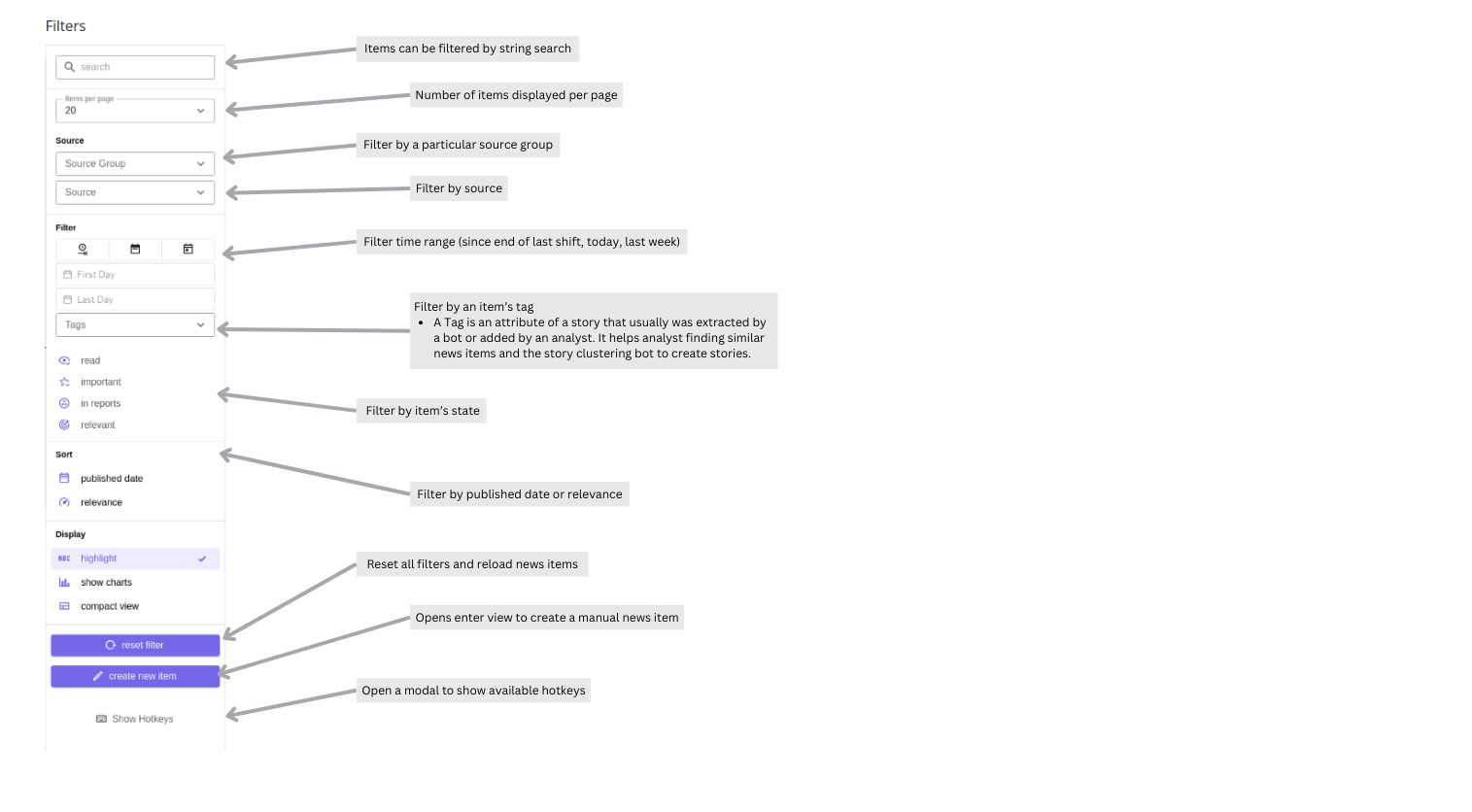
For manually created stories, the “updated” timestamp is essentially the creation time. As a result, filtering by Last day for a manually created story will not return it, even if an older “published date” is set.
News items collected by Collectors become visible in the Assess section. These items can later be grouped by context, either automatically by the Bots or manually.
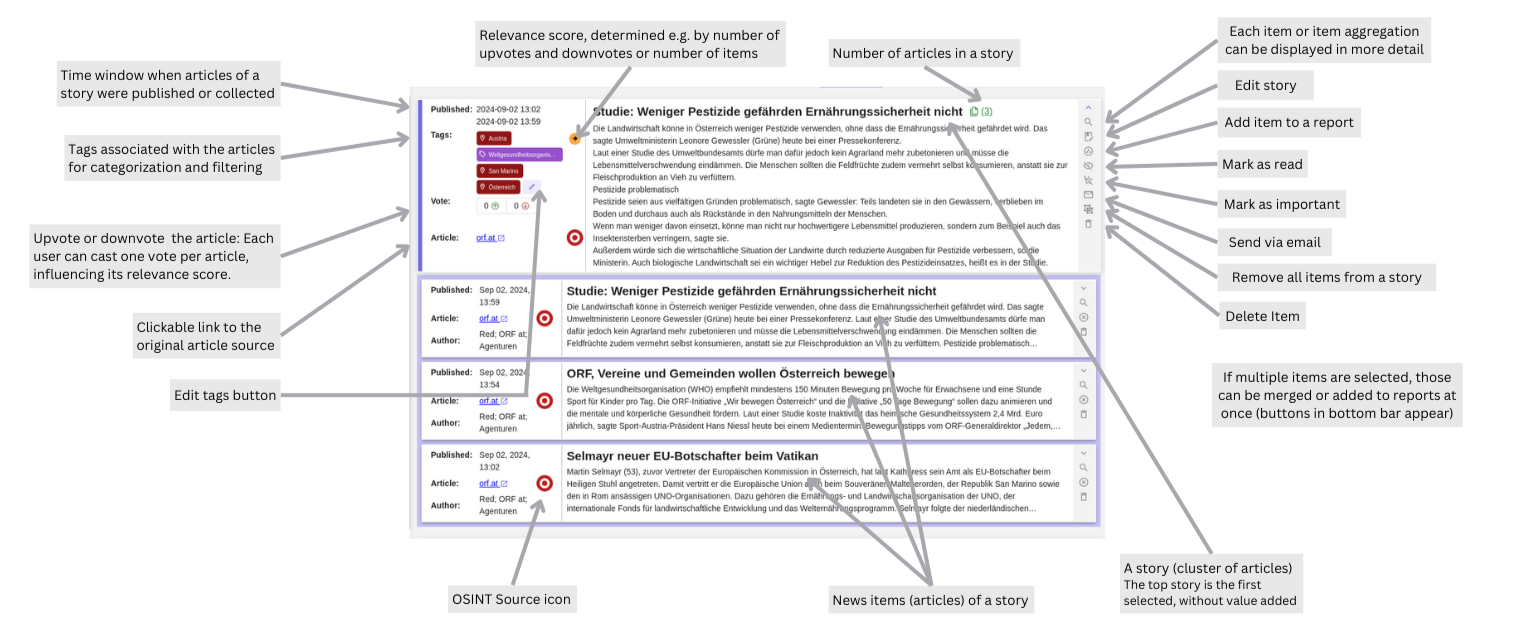
Detail view:
Charts:
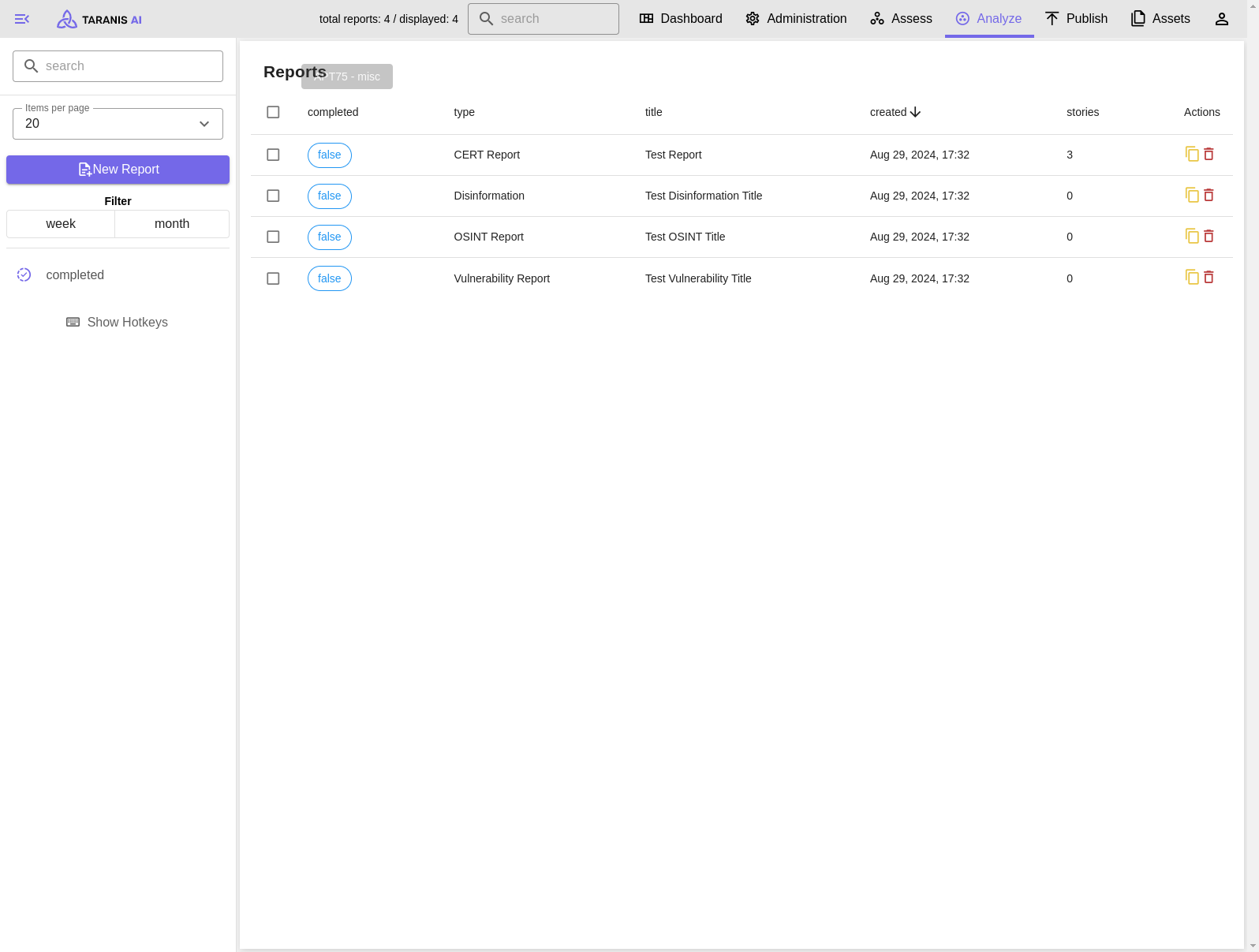
Different types of reports can be created. Those types can be managed by the admin user in the Administration/Report Types endpoint (see Report Types).
After one of the next releases, it will also be possible to create products from reports.
Reports can be set to “completed” by changing the switch button in the report edit view (top right).
Incomplete reports created today
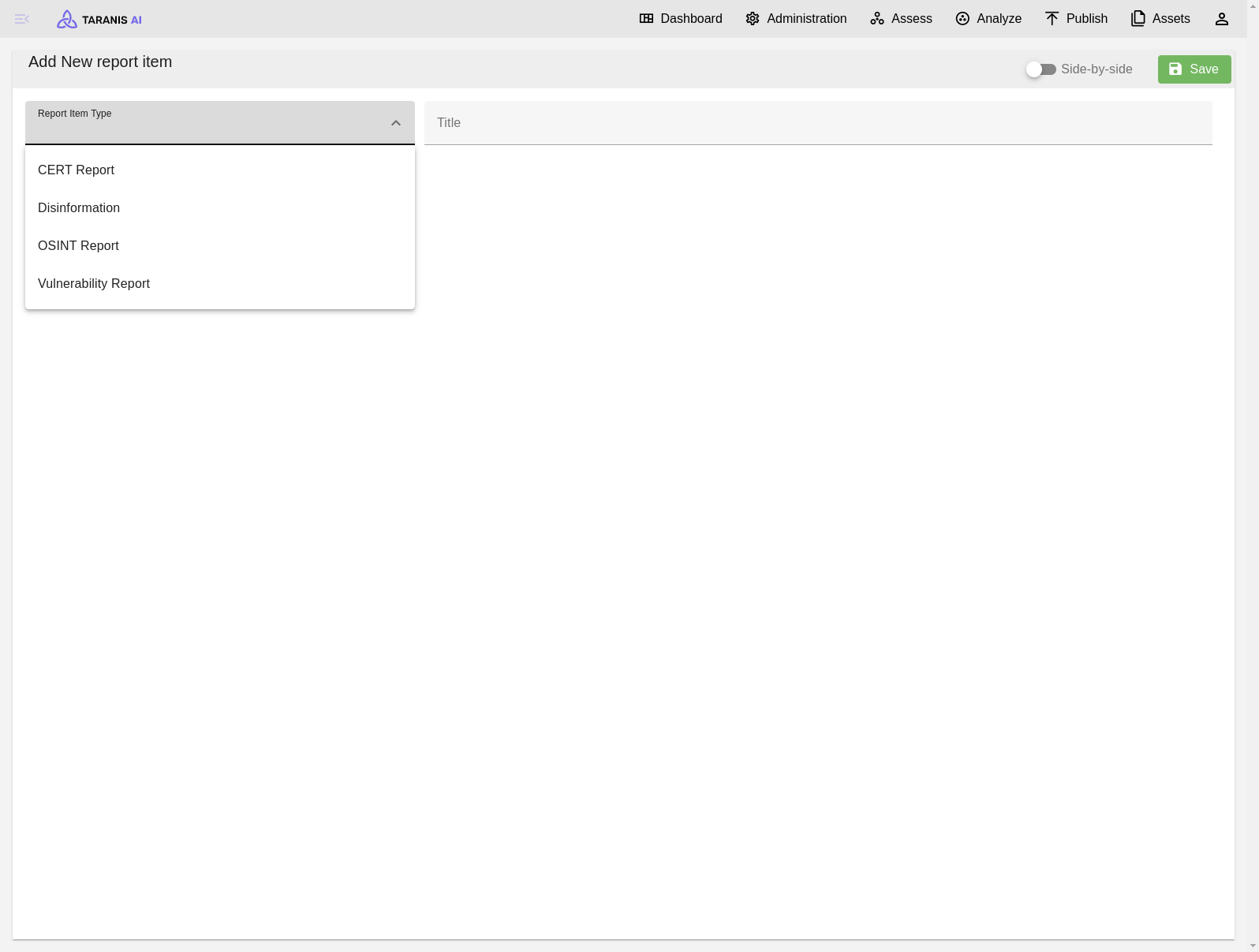
Add new report item
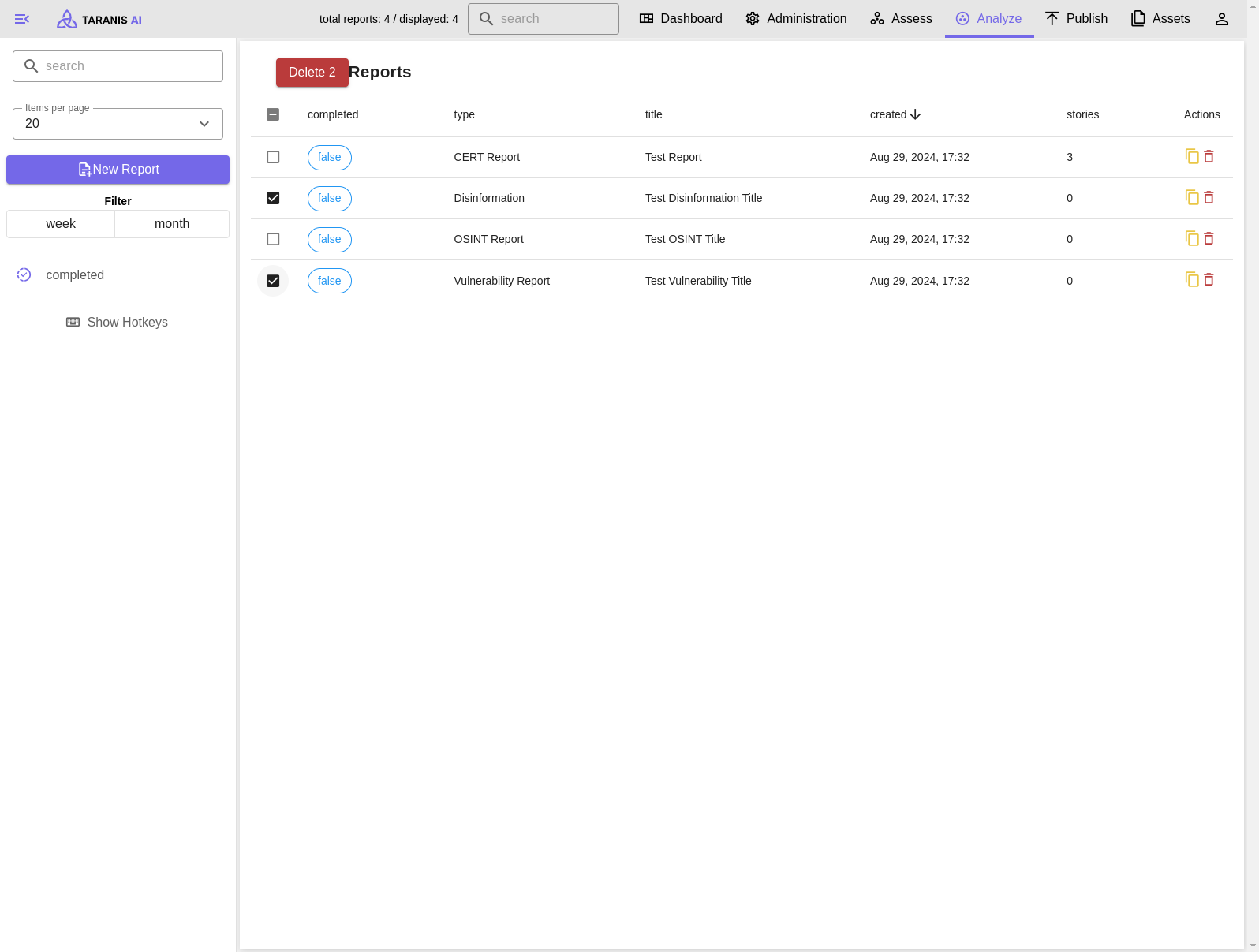
Deleting multiple reports at once
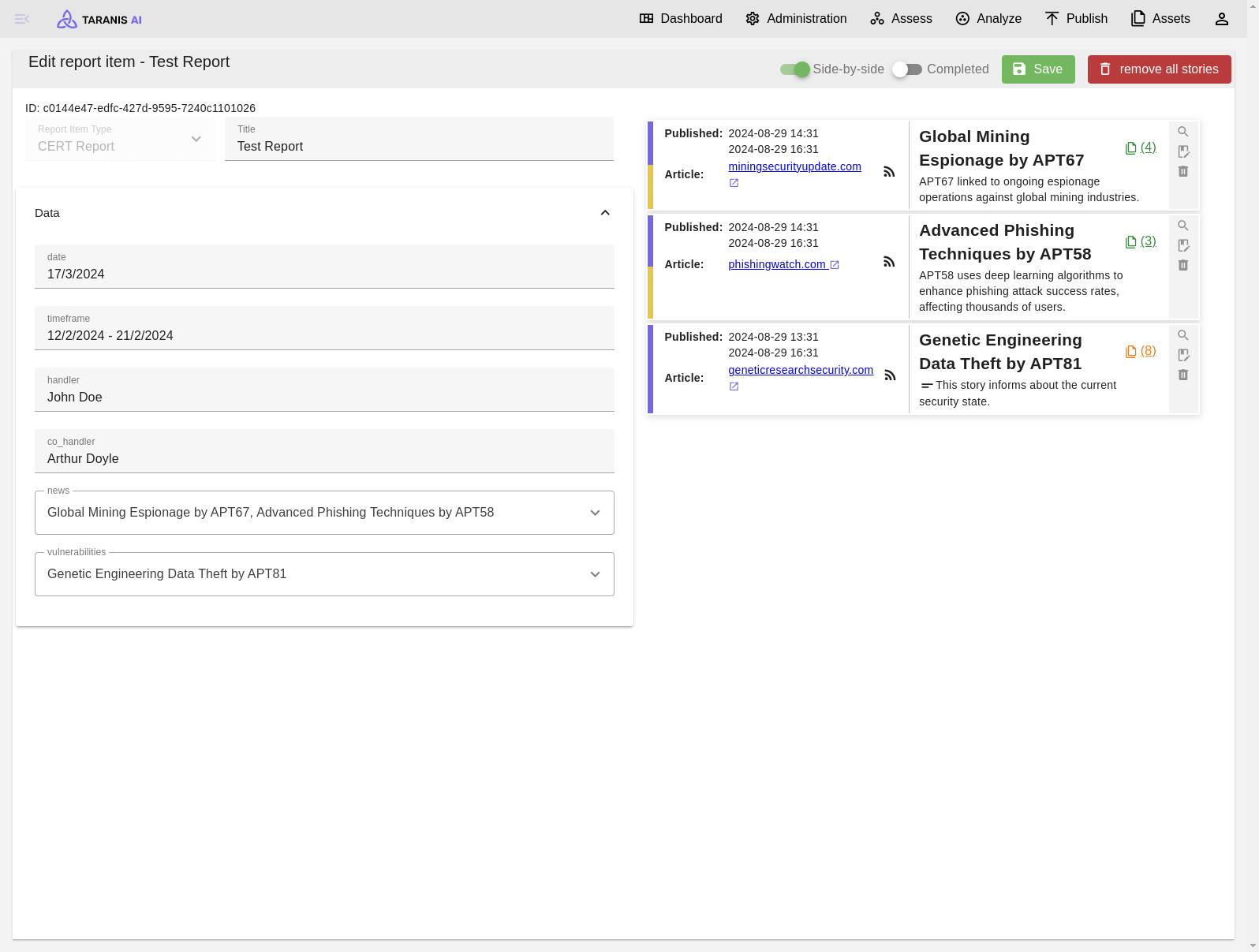
Report item view
Description of options of the left-hand side panel.
See also Product Types_
Dashboard is displaying the most frequent topics as well as basic statistics of the application. By clicking on one of the topic headers, the user gets redirected to the Assess endpoint (with the topic set as tag filter). The statistic fields redirect to the respective endpoints, too.
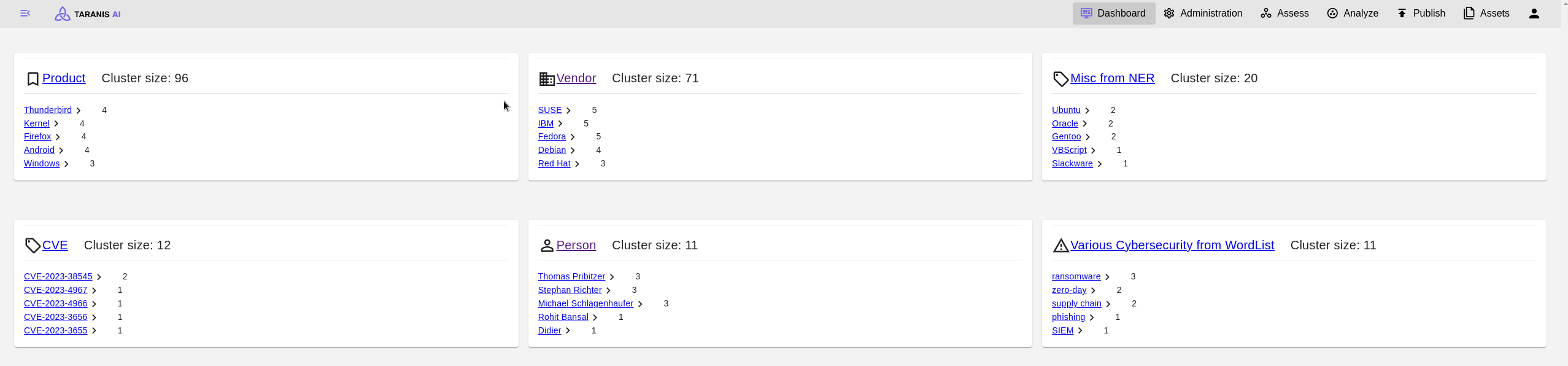
Username and user’s organization are displayed.
These options are accessible only via users with respective administration privileges. (See User management)
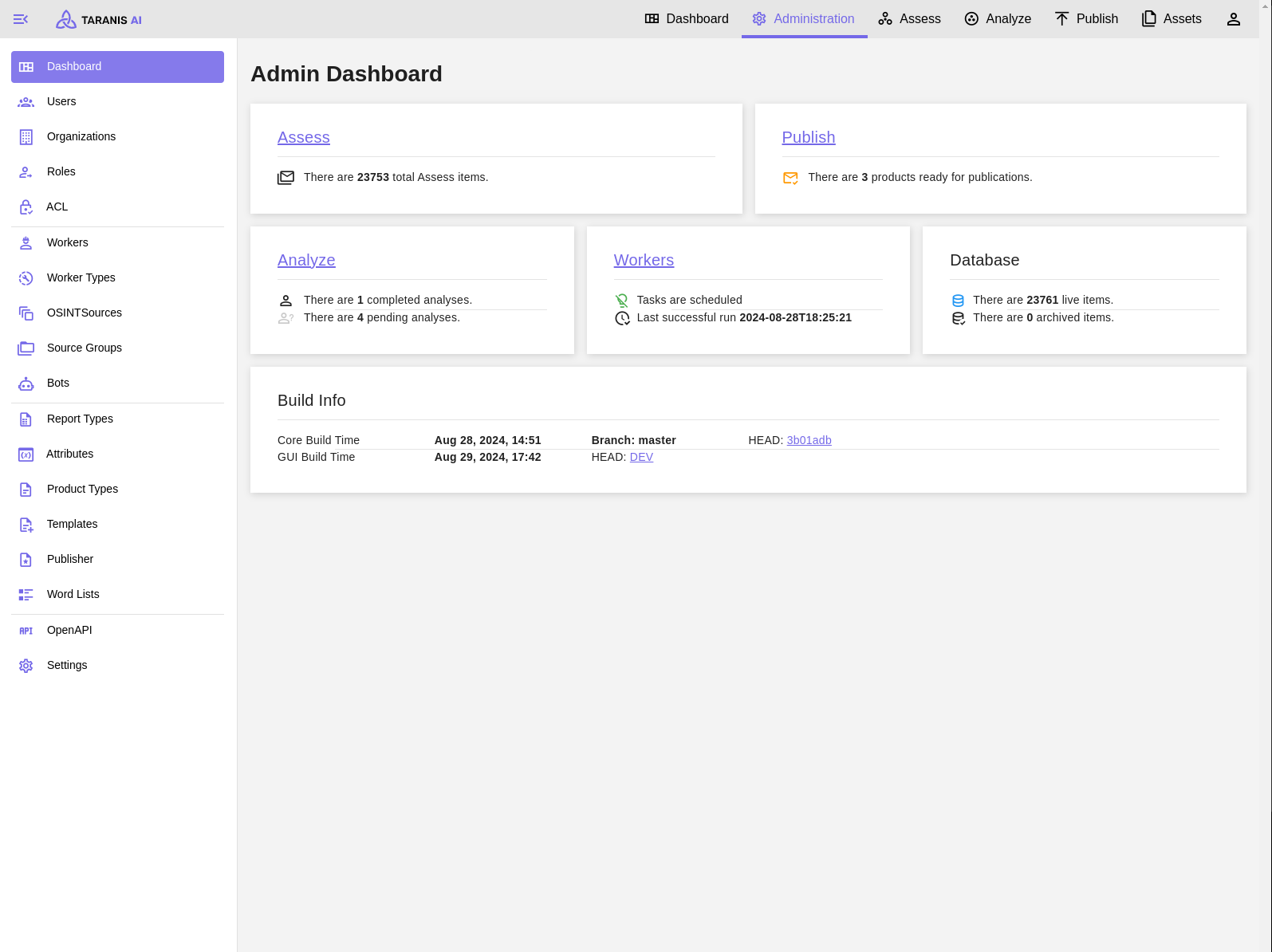
Administration dashboard showing statistics and all its functionalities (sidebar)
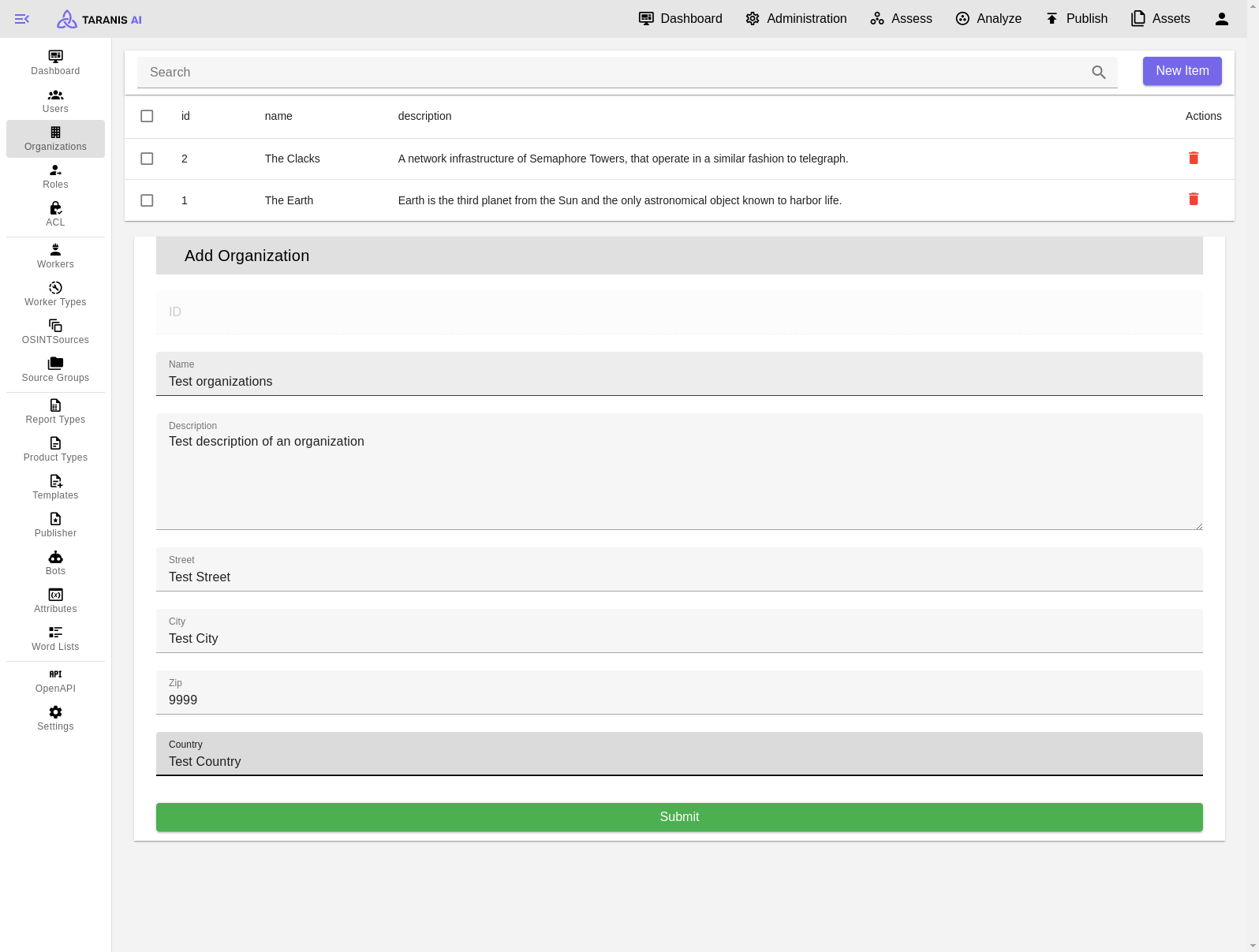
Organizations can be added with following parameters defining them: name, description, address.
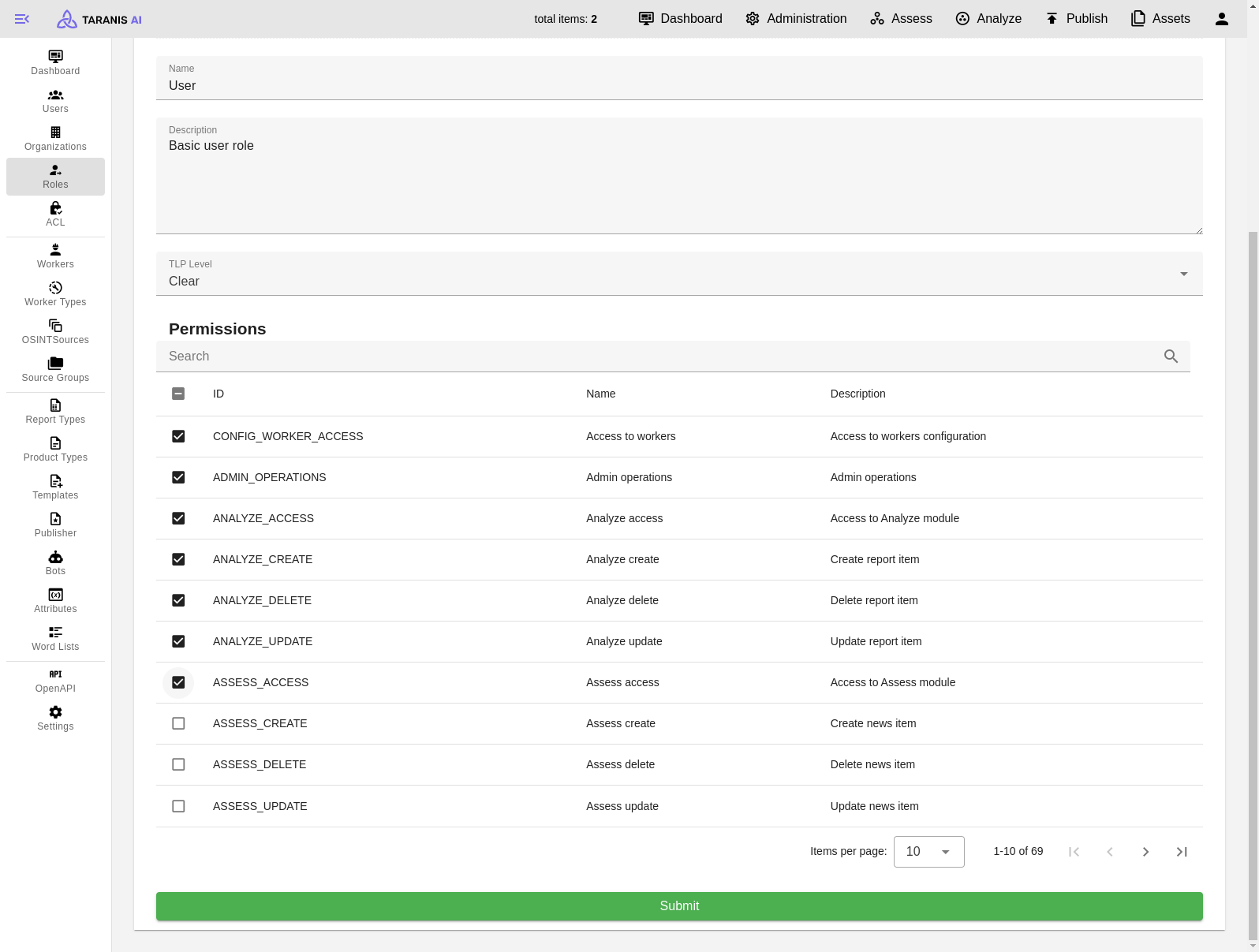
Define roles with certain permissions.
Manage users and assign them a role, permissions and an organization.
Add new Organization
Edit basic user role
Add new User
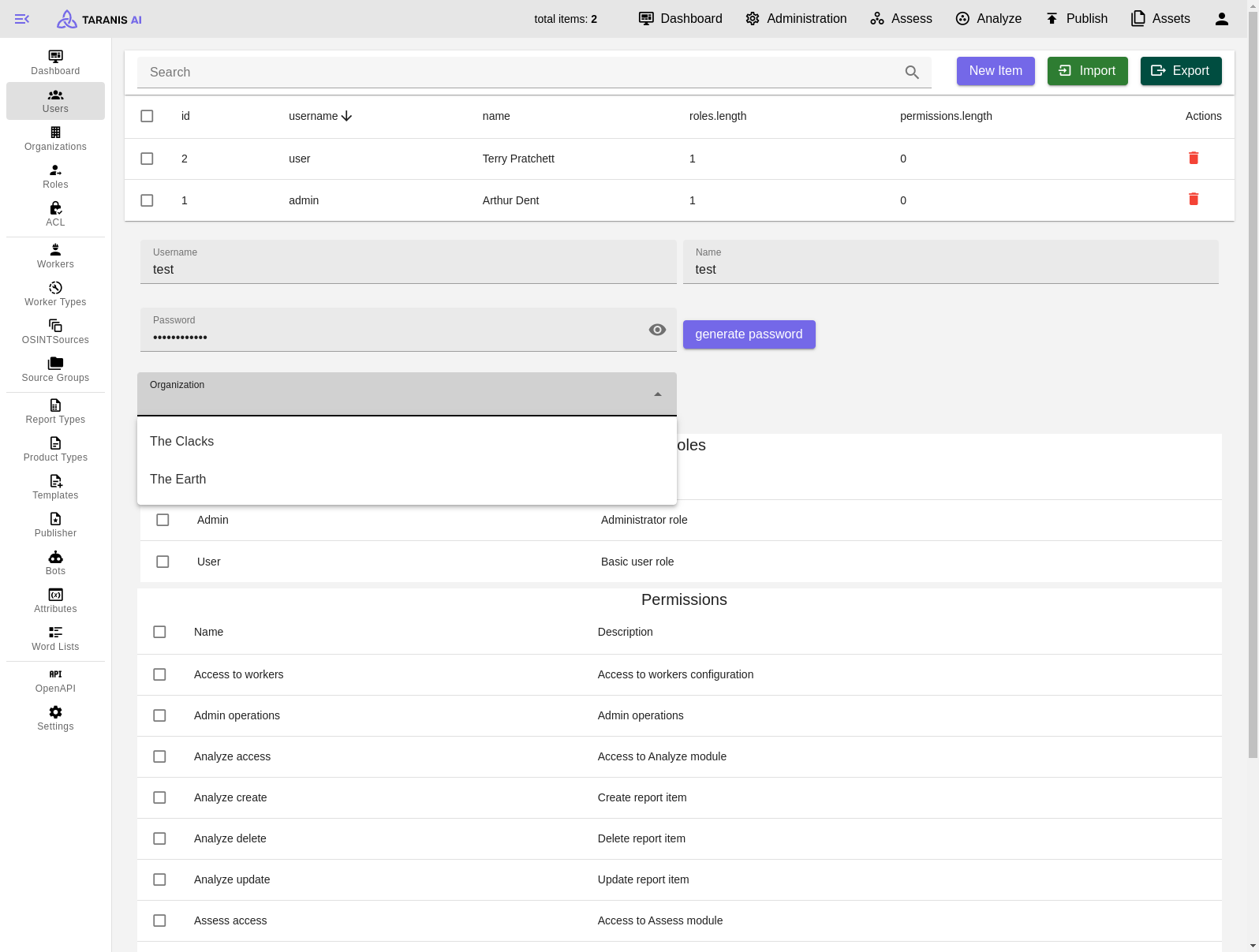
To get started there is list of RSS sources we worked with: Initial setup
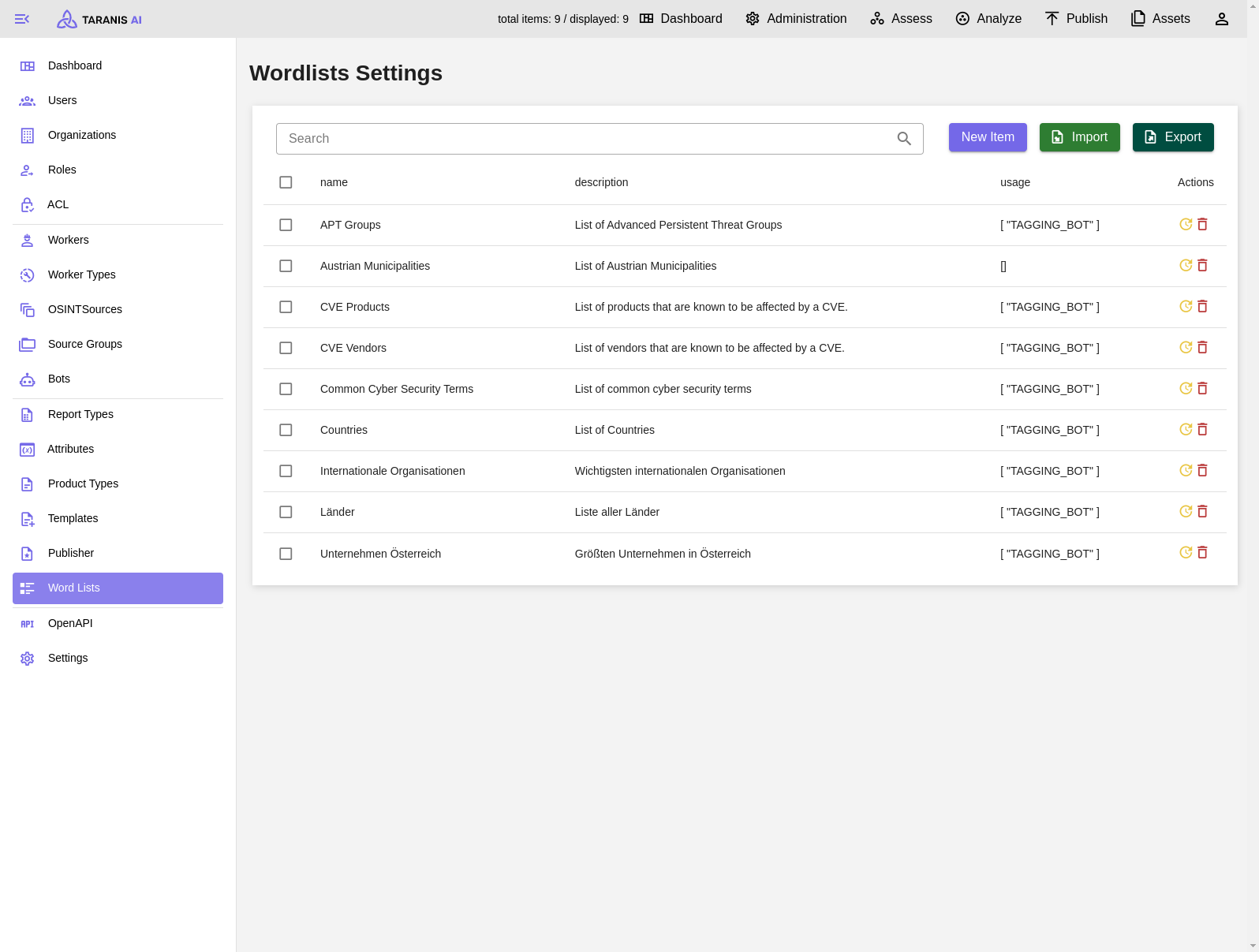
Word lists can have the following functionalities (displayed under “usage”):
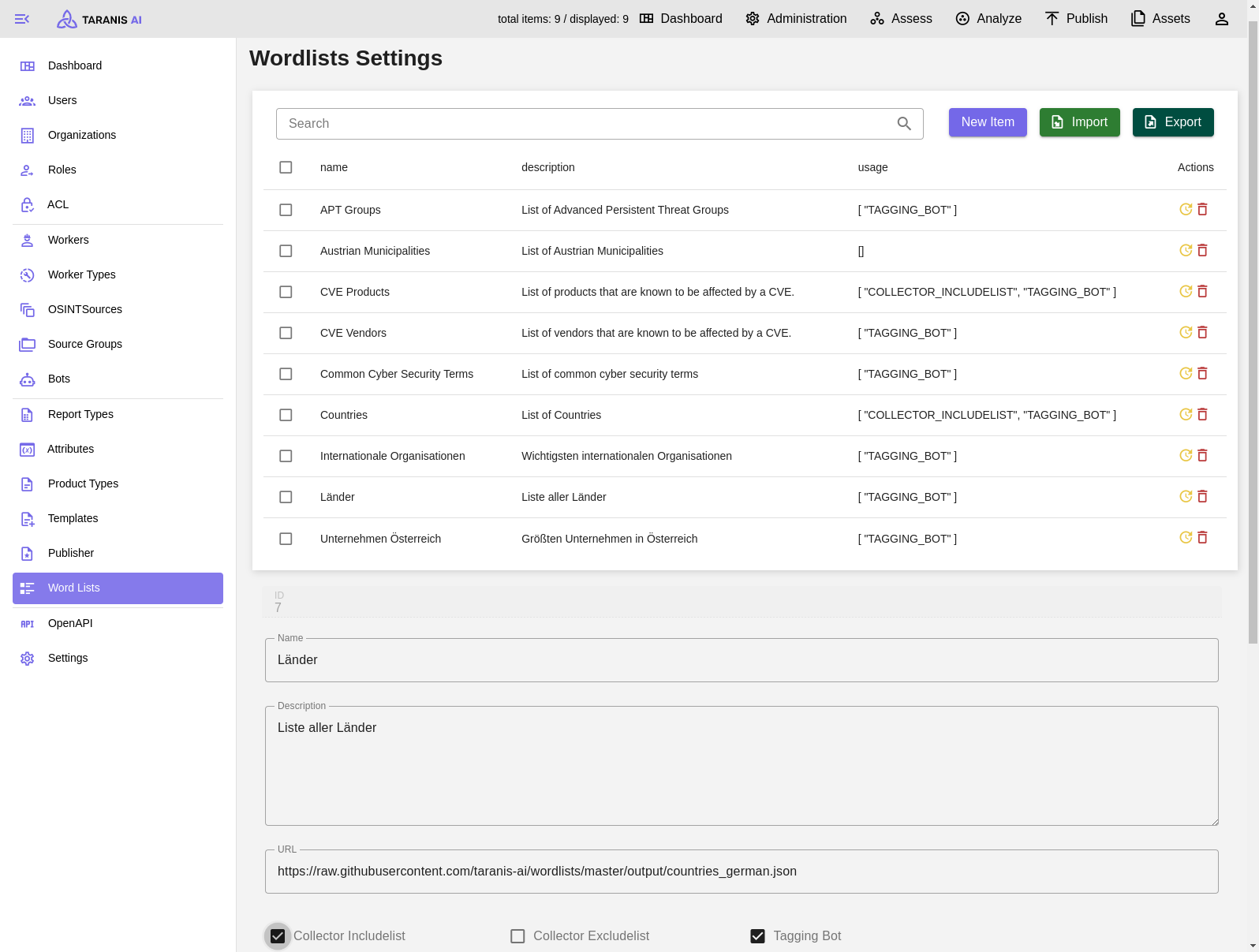
To activate include or exclude lists, they need to be added to the default source group.
It has to be mentioned, that this include/exclude filtering happens during the news item collection. Therefore, only filtered news items will be stored in the database and displayed in “Assess”.
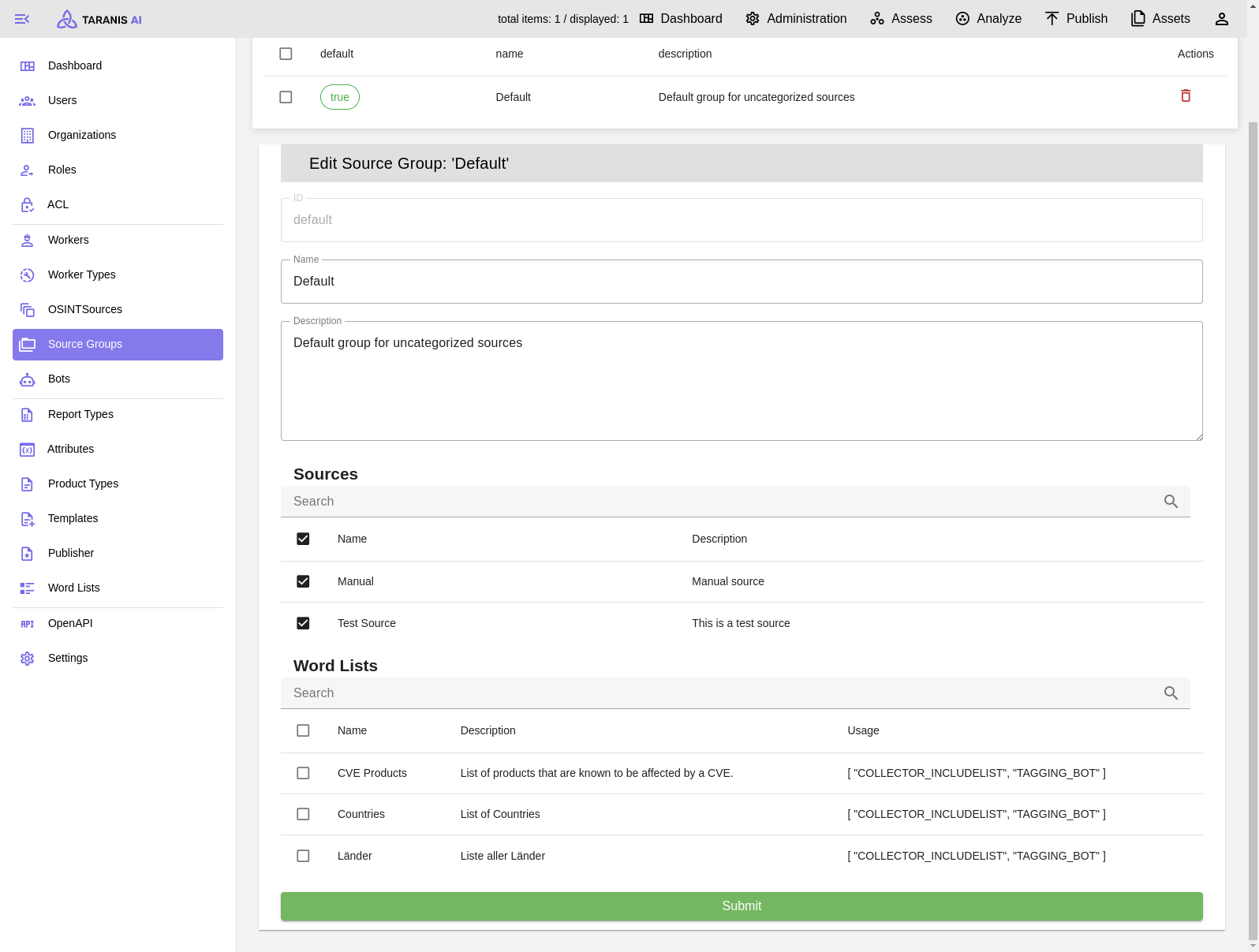
After the collection, it is possible to adapt news items.
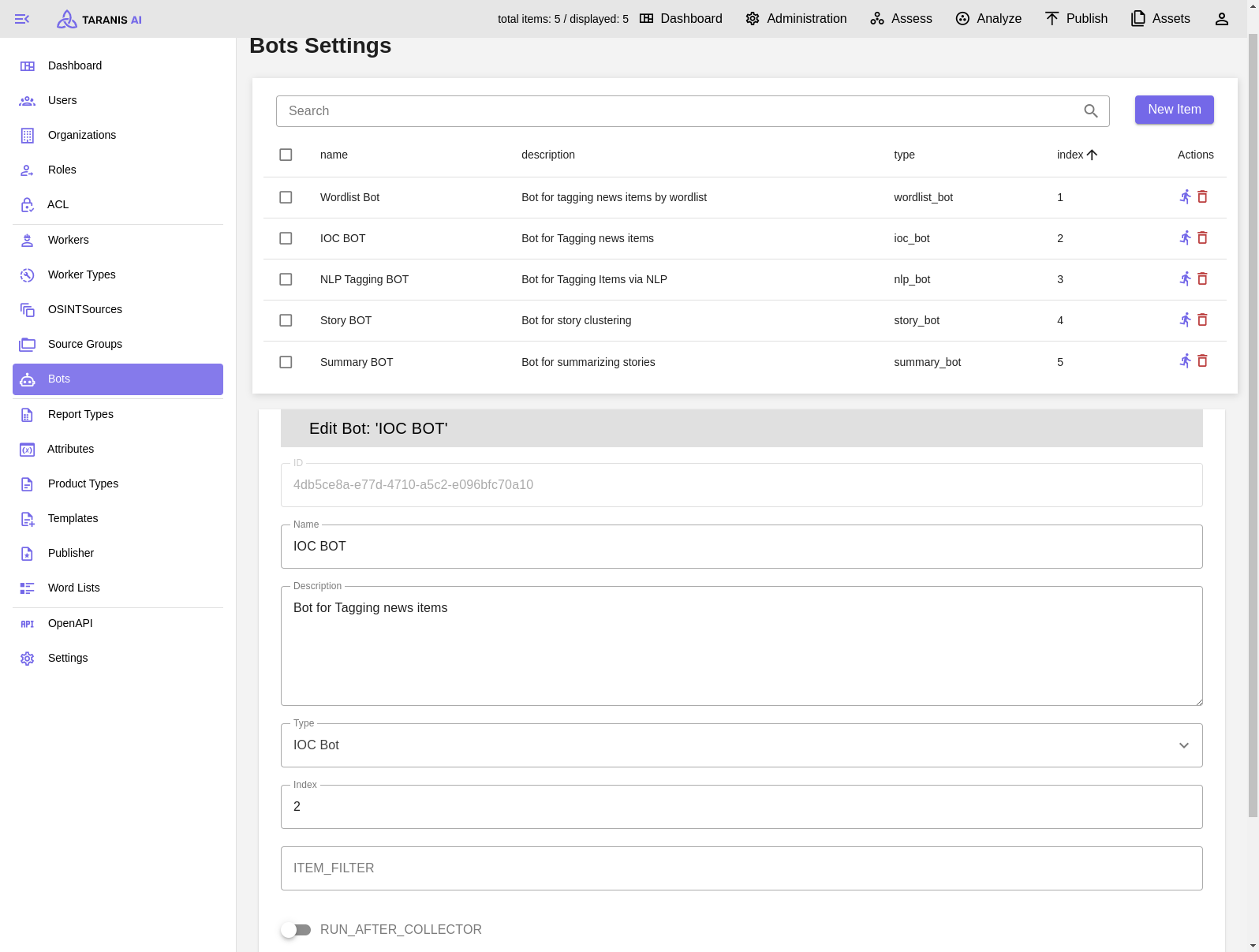
Therefore, following bots are currently available:
CRUD: Bots can be created, updated and deleted.
Index: Decides the order of bots
RUN_AFTER_COLLECTOR: Indicates if bot is active after collection
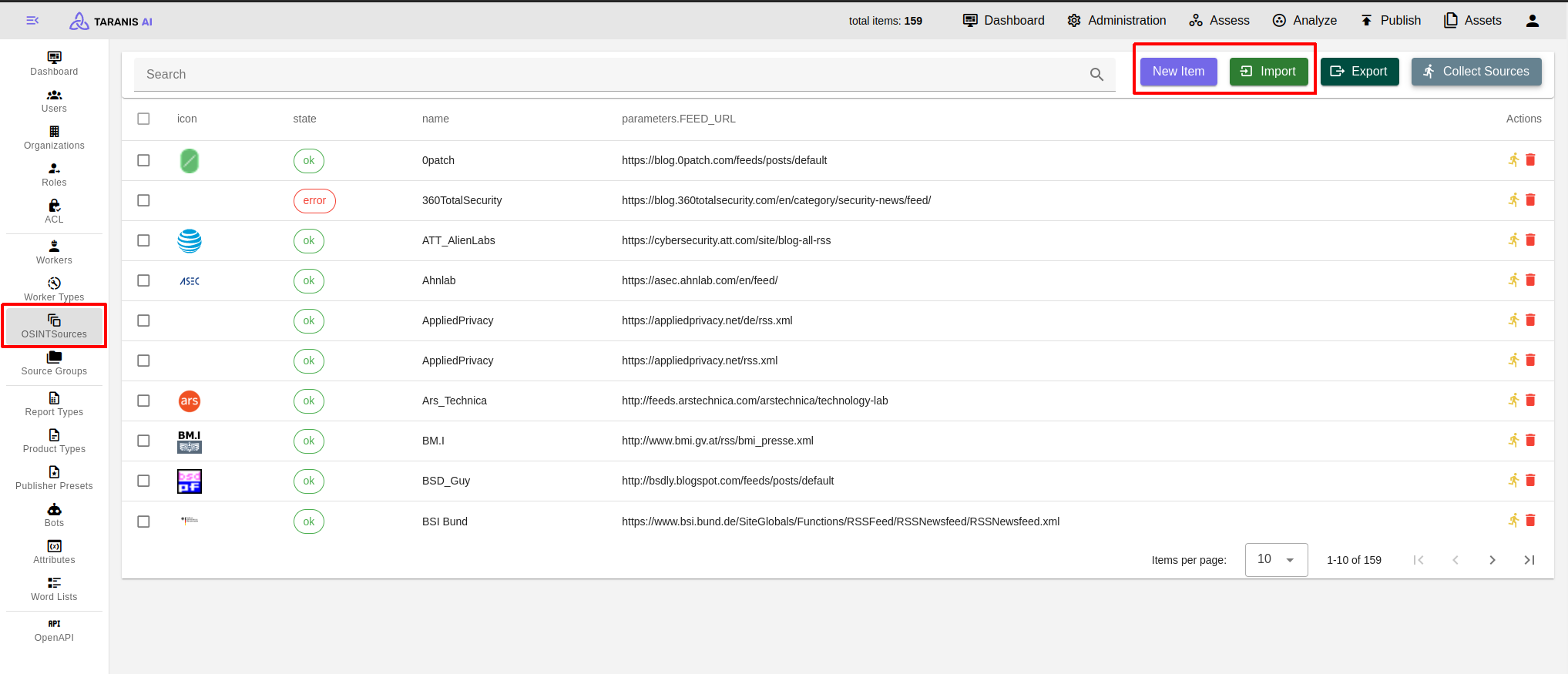
After all settings are made, sources can be collected. Either collect all sources by clicking on the “collect sources” button, or collect single sources.
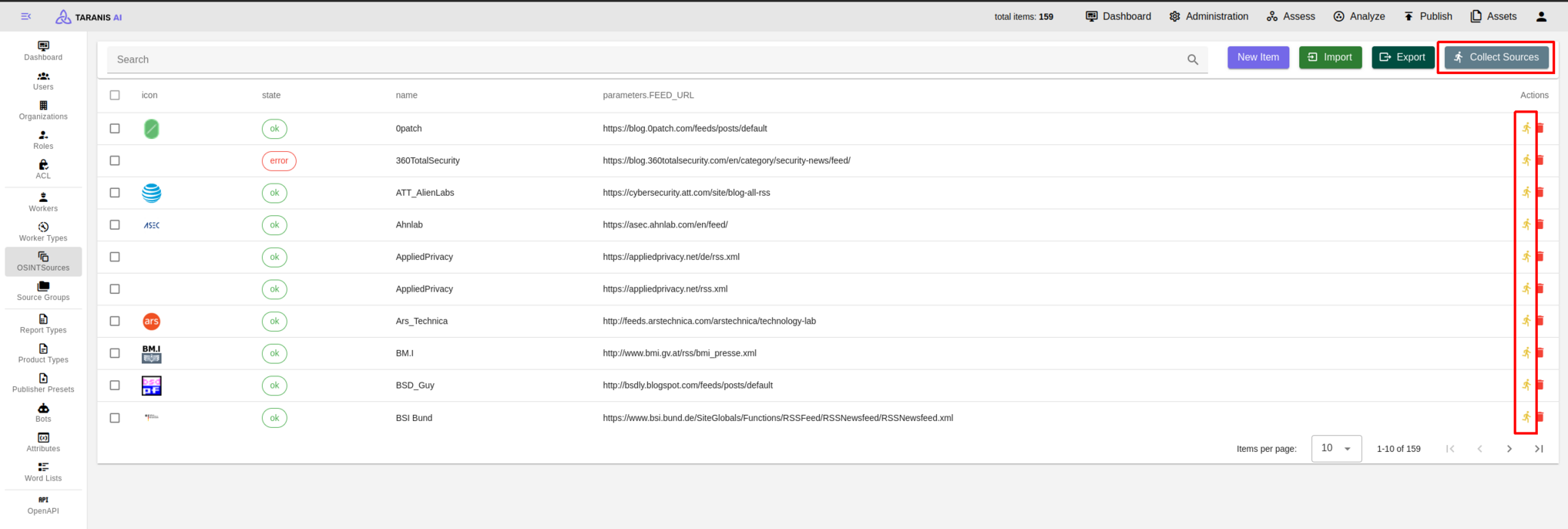
Sources for gathering data are set in the OSINTSources. It is possible to:
Select Import and choose desired JSON file for import. (See Initial Setup)
Select Export to download a JSON file containing your established collectors.
Select Collect Sources to aggregate information from all established OSINT sources.
When creating new Reports, one of the created report types have to be selected (see Analyze).
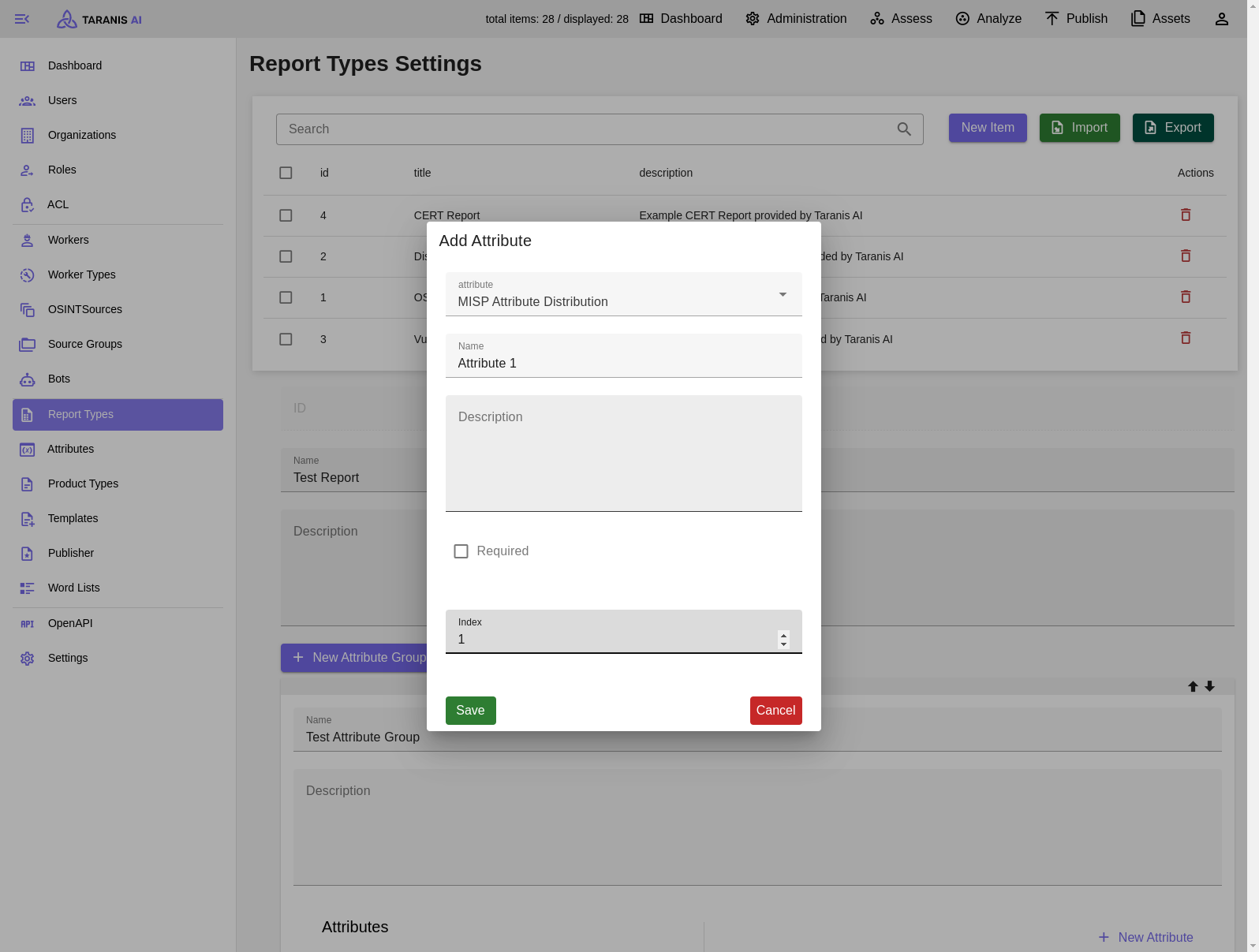
Desired attributes need to be created first. Then they can be managed by the admin user. Besides name, description and default value also type, validator and validator parameter can be set.
Add new Attribute
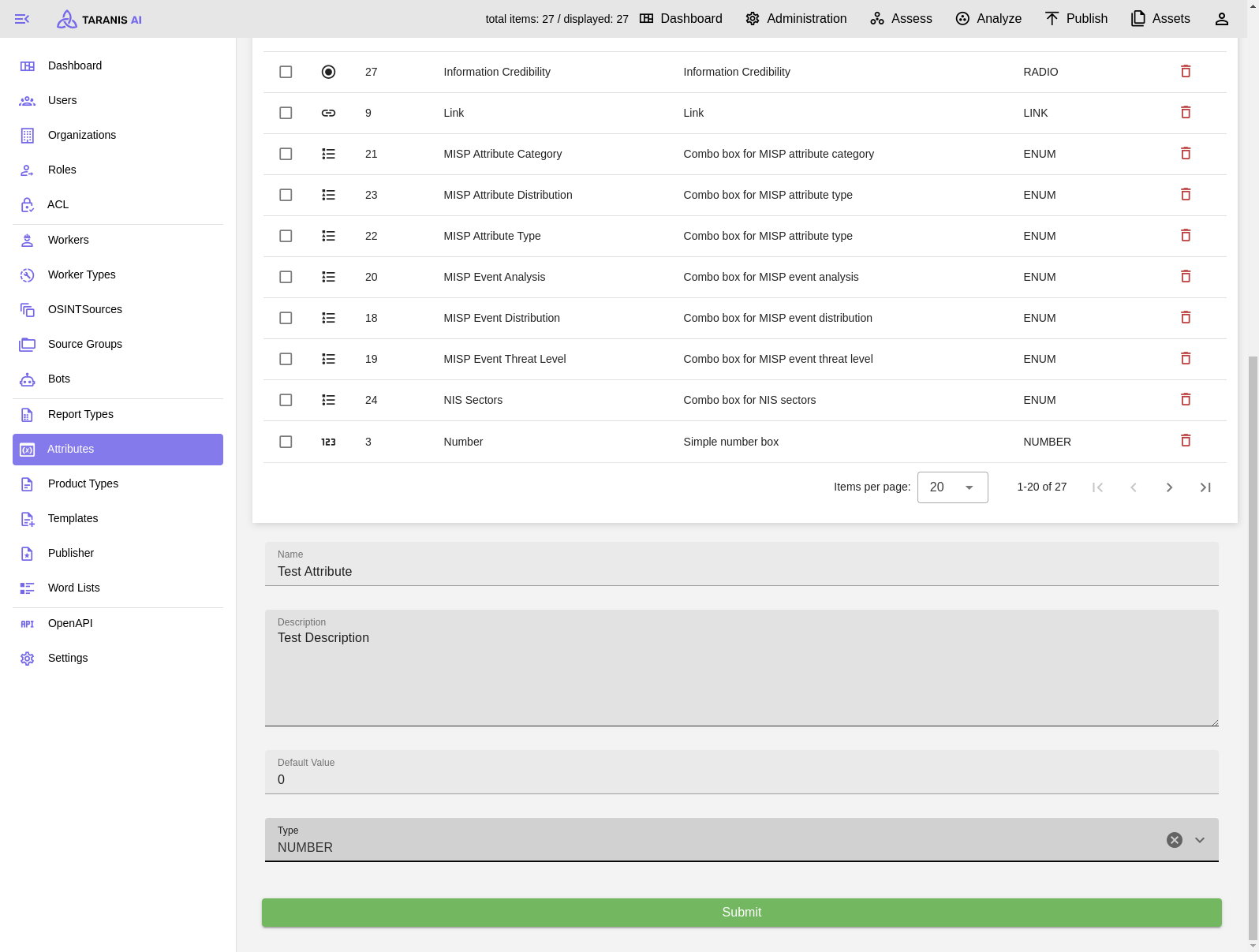
Report Types - Create new Report Type
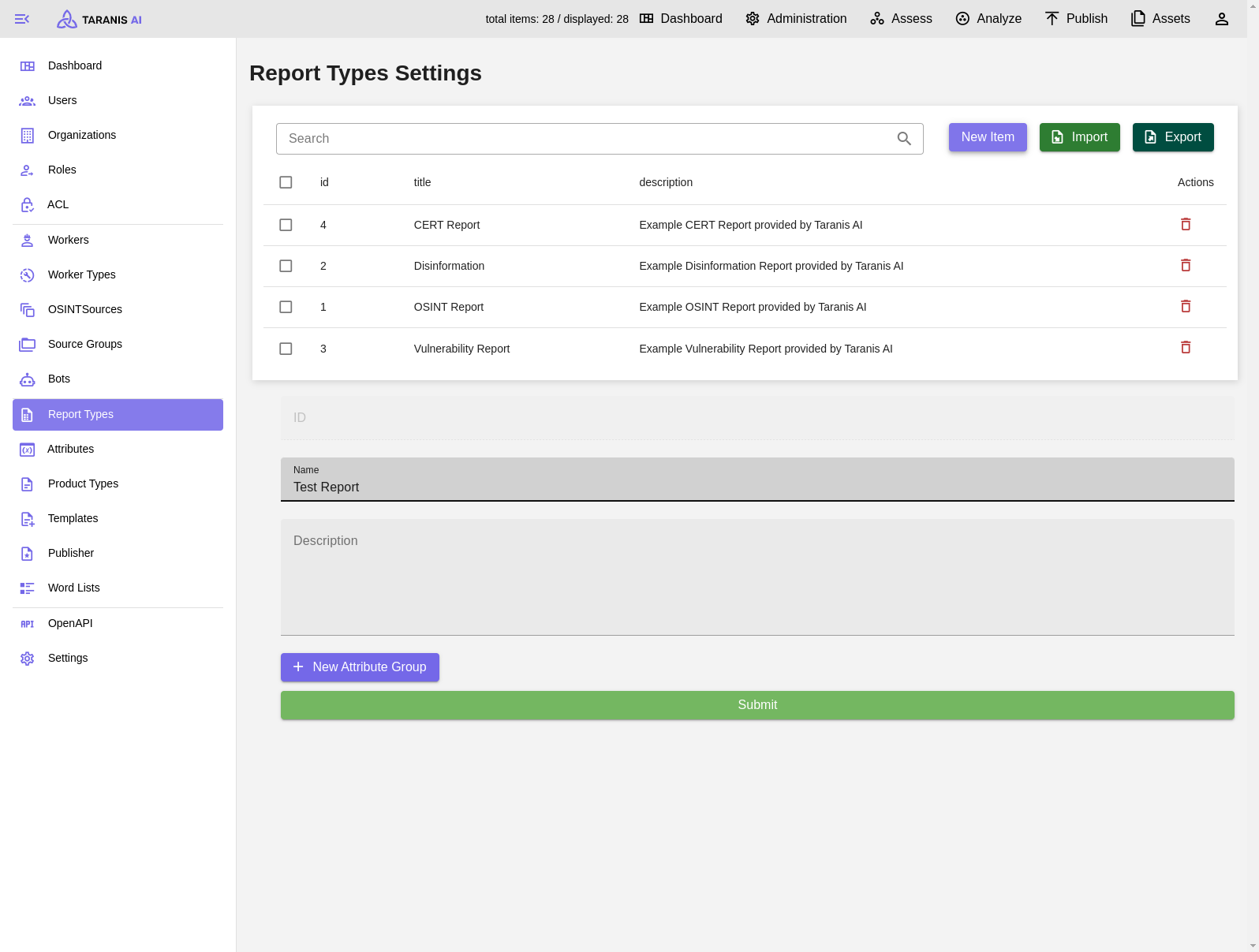
Report Types - Add new Attribute Group
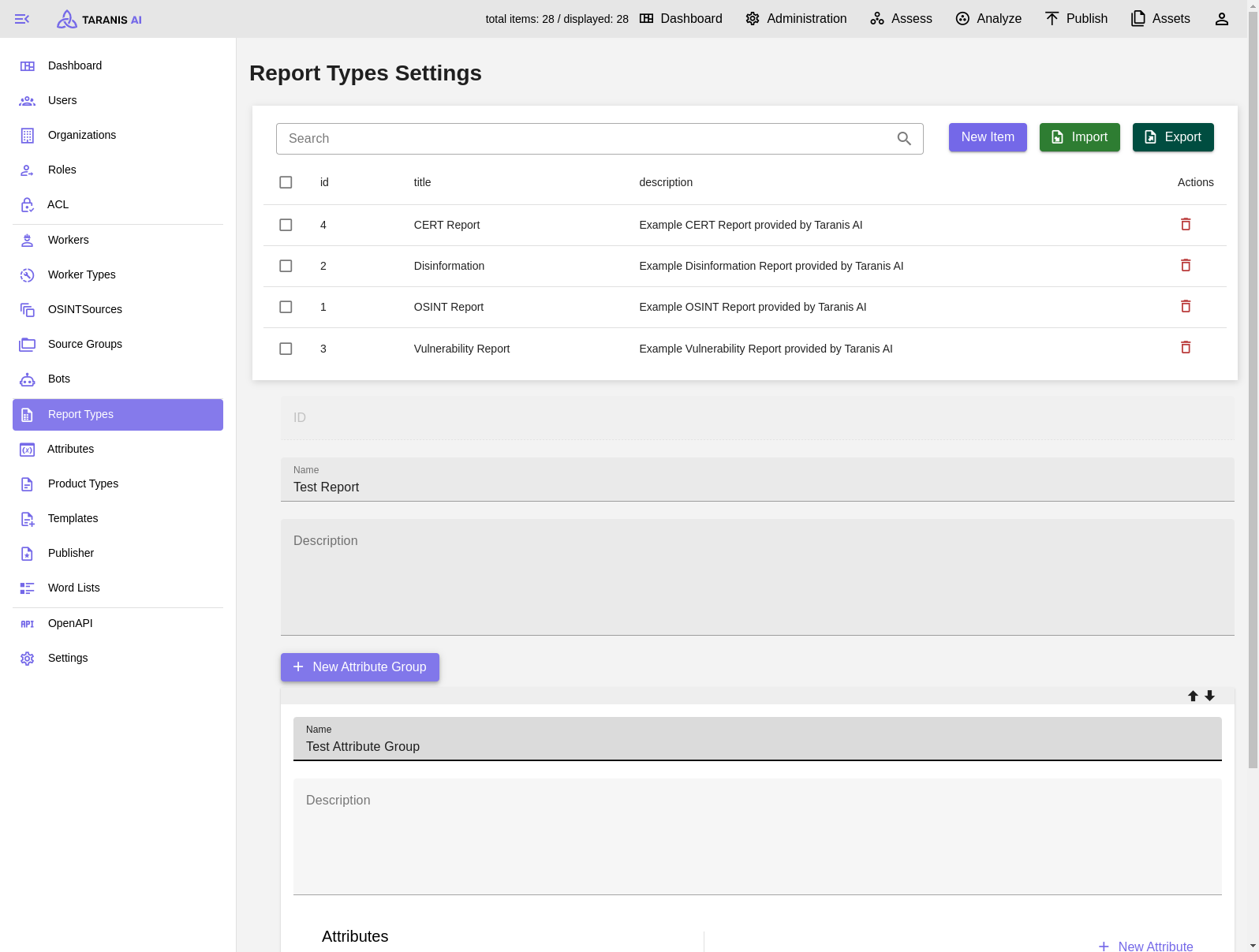
Report Types - Select new Attribute from list
0 */8 * * *).The administration view now allows users to use the Preview feature to see the result of the configuration without the items being processed further for the Assess view. This feature is available for RSS, Simple Web and RT collector.
RSS Collector enables Taranis AI to collect data from a user-defined RSS feed (See RSS feeds details).
PROXY_SERVER field, use what is currently set as a default in Settings; learn more in section Settings)json] (can be used to add additional headers, not all headers work as expected)key of the feed schema, from where the content for news items should be extracted (e.g. description of the feed entry); if the key for a feed entry is not found, it falls back to behaviour, as if the key was not entered at all)Summary field of RSS feed)The RSS Collector supports the use of XPath for locating elements. (See Simple Web Collector Advanced configuration)
{ "AUTHORIZATION": "Bearer Token1234", "X-API-KEY": "12345", "Cookie": "firstcookie=1234; second-cookie=4321", }Simple Web Collector enables Taranis AI to collect data using web URLs and XPaths.
The simplest way to use this collector is to use the WEB_URL field only. By using only the WEB_URL field, Taranis-AI autonomously determines the content to be collected. Even though it is mostly reliable, sometimes it is not perfect.
When content cannot be reliably collected using the Basic configuration, adding the attribute XPATH (See tutorial how to find it), can be useful. It is crucial to specify the XPath of the precise element containing the desired data.
To set up an RSS Collector for collecting posts from a Mastodon hashtag or user, follow these steps:
Finding the Mastodon RSS Feed URL:
.rss to the hashtag URL. For example, to collect posts tagged with #cybersecurity:
https://mastodon.social/tags/cybersecurity.rss.rss to the user’s profile URL. Example:
https://mastodon.social/@username.rssCreating a New RSS Source with Required Parameters: When creating the new RSS source, configure it with the following parameters. Here’s an example of how to fill out the fields:
https://mastodon.social/tags/cybersecurity.rss)."summary" to specify the main content location within each RSS entry."false" since we’re not splitting entries into multiple items.Extend your compose.yml with a tor service, e.g.
tor:
image: "docker.io/dperson/torproxy:latest"
deploy:
restart_policy:
condition: always
environment:
# LOCATION: "AT"
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "200k"
max-file: "10"
Read details about the used docker image here
The important setting is “PROXY_SERVER” in the OSINT Source you want to crawl.
RT Collector enables Taranis AI to collect data from a user-defined Request Tracker instance.
RT Collector collects tickets, translates all ticket attachments into individual News Items. A ticket is represented via a Story. It also collects ticket Custom Fields and saves it as key-value pairs represented with Story attributes, visible whilst Story editing. On each collector execution an update to existing Stories occurs, so editing the Story values in Taranis AI is not recommended and handling it more like read-only items is better.
Required fields:
http://localhost).Optional fields:
Until the definitions of our MISP Objects are not officially part of the MISP platform, feel free to import them manually (see MISP Objects). This allows to edit the information of News Items and Story data directly in the MISP instance without Taranis AI.
MISP Collector enables Taranis AI to collect MISP events.
Required fields:
https://localhost)Optional fields:
Essentially it works exactly like other collectors with one exception: conflicts. Given the nature of the collaborative environment of MISP events (they can be changed in the MISP platform by the owning organisation and secondary organisations can submit change requests using the MISP proposals). Due to that, there will likely occur conflicts when attempting to update existing Stories that were, in the meantime, internally modified.
Generally, conflicts occur the moment, a Story is modified internally, and has not been pushed to MISP immediately. Therefore, it is recommended to always try to keep Stories in sync with the MISP events. To update them in MISP with the Story (see Connectors).
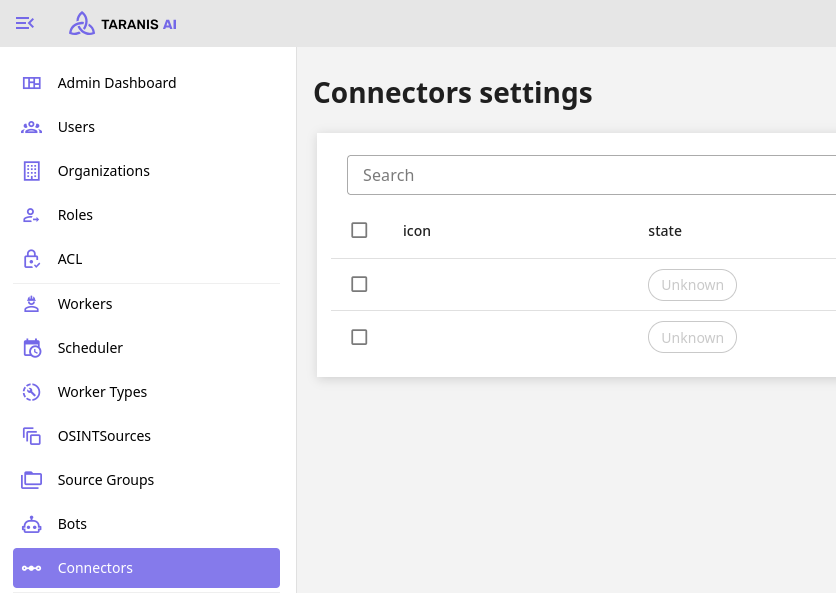
Conflicts can currently be resolved in the Connectors section accessible in the general and administration dashboard.
In the Conflict Resolution View it is possible to resolve given conflicts.
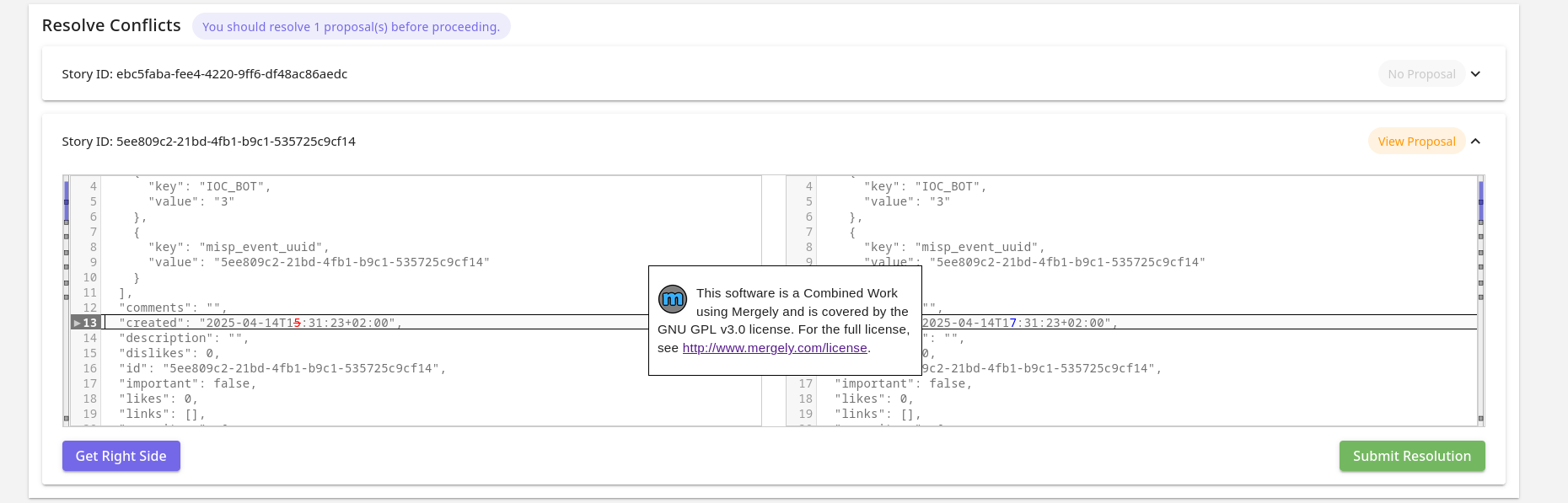
In the view, all stories that have conflicts will be shown in expandable cards. One by one it is possible to inspect them and resolve them.
At the top, the number of events (among the ones in conflict) have proposals to resolve is shown (only owned by your MISP organisation). It is recommended to resolve them first in MISP, before you resolve them in Taranis AI, so you work with the latest information. Once teh conflicts are resolved and changes are submitted, the Story will be updated without raising conflicts later on (until the Story gets modified internally). It is the users’ decision, whether they want to resolve the conflicts immediately with the version collected without proposals, or are skipped, preposals in MISP are resolved, and resolve conflicts later on next collection. In case a Story has proposals, it is possible to open the event in MISP with the “View Proposal” button.
The content on the left is the current Story. The content on the right hand side editor is the new content and is the content, which is the content that is used for the eventual update. It is possible to take the right or left side of each difference shown using the diff window by clicking the arrows on the left sides of each content window.
Both sides are freely editable and keyboard shortcuts for back and forward are supported. The context for keyboard shortcuts is decided based on where the cursor is (where it was clicked the last time - right or left side).
It is important, that the content on the right side stays a valid Story JSON.
With “Get Right Side” button, it is possible to check what content will be submitted. “Submit Resolution” button is used to submit the update.
Conflicts are stored in a temporary memory, to encourage a fresh MISP Collector recollection, before resolving conflicts and to prevent conflict resolution with outdated data.
Digest Splitting is a feature that allows the user to split all available URLs in the located element into individual News Items. The Digest Splitting Limit is the maximum number of URLs that will be split into individual News Items. If the limit is reached, the remaining URLs are dropped. The Digest Splitting Limit is set to 30 News Items by default but can be adjusted by the administrator. Useful in case of timeouts during collection of too many News Items.
Collectors will fail if the web page content is only available with JavaScript. In that case it is possible to turn on the Browser Mode. All requests will have JavaScript enabled, therefore, it is slower and can use more resources.
Supported options:
The MISP connector is currently in an experimental stage. Please submit issues when you discover any problems or need support with its usage.
Until the definitions of our MISP Objects are not officially part of the MISP platform, feel free to import them manually (see MISP Objects). This enables you to edit the objects of News Items and Story data directly in you MISP instances without Taranis AI.
MISP Connector enables Taranis AI to push Stories to MISP in the representation of MISP Events.
The created events contain automatically an Event Report based on the Story content (currently it encompasses the Story description and Story summary, if you feel the Event Report would benefit extending with more information, please open a feature request for it here).
First the user with administrative privileges needs to make sure, the permissions connected to Connectors usage are assigned appropriately, by default, they are not assigned to any user, not even the admins themselves. Then the Connector needs to be setup in the Admin section under the Connectors tab.
Explanation of individual permissions:
Required parameters:
https://localhost)Optional parameters:
To send a story to MISP, use the button “Share to Connector” in Story options in Assess. When an update to the Story is later on made, it is recommended to share the change immediately, you need to do this manually like the first time.
Before a Story is pushed repeatedly to update the MISP event, it is important to check if any proposals are pending in the MISP event, as it would override the original content of it and would make it difficult to resolve the proposals correctly.
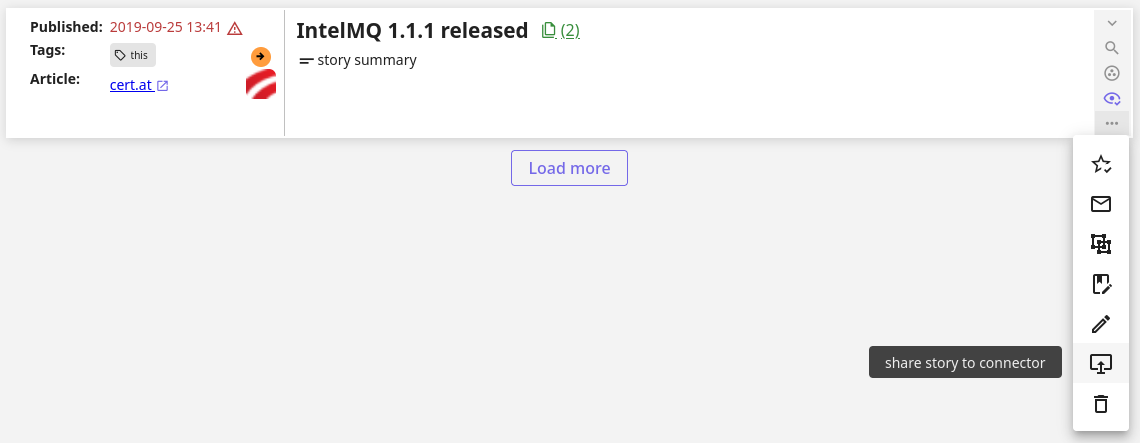
When a Story is collected, that is not owned by your configured organisation, it is possible to update it in Taranis AI and by using the same “Share to Connector” button in the Story options a proposal to the event is created. Then the owning organisation should review this proposal, and approve or reject the changes.
The Email Publisher allows sending out Products.
Note: The EMAIL_SENDER and EMAIL_RECIPIENT parameters are used to construct the message envelope used by the transport agents. Message headers are not modified by these parameters in any way.
Required fields are marked with a *.
Once the publisher is created, it becomes available in the “Publish” section of each product. To send out a product via email, the product must be “Rendered” first. To render a product, use the option available in the product’s view.
All crucial fields are editable, with the most important being Type, Template, and Report Types.
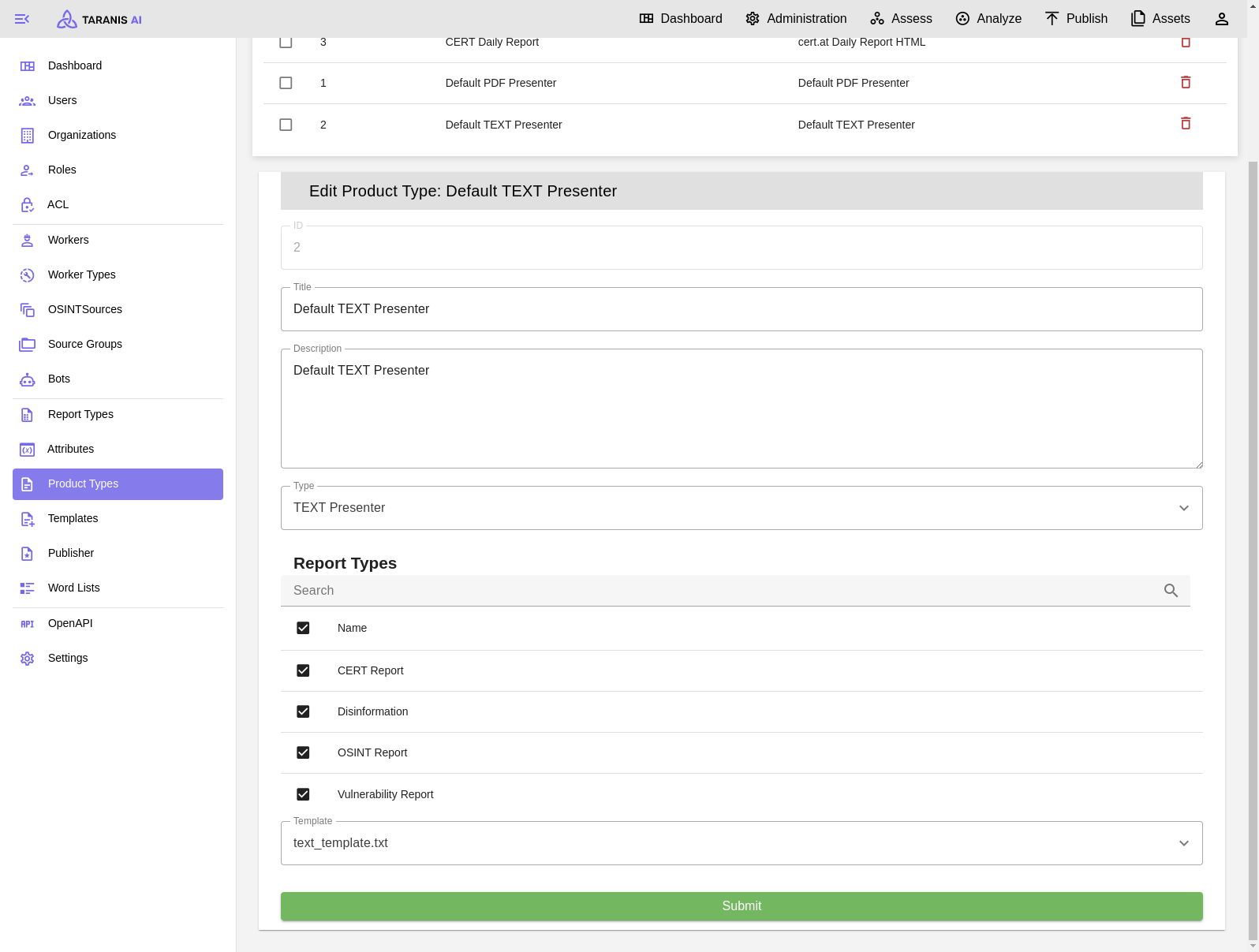
While there are several prebuilt product types available, users also have the option to create their own product types using custom templates.
It can be beneficial to create custom Product Types to meet desired results with the publishers.
This is an example to render arbitrary values and loop over attributes.
src/core/core/static/presenter_templates,TITLE: {{ data.report_items[0].get('title') | default('No title provided', true) }}<br>
DATE CREATED: {{ data.report_items[0].get('created') | default('Not available', true) }}<br>
LAST UPDATED: {{ data.report_items[0].get('last_updated') | default('Not available', true) }}<br>
{% for name, attribute in data.report_items[0].get('attributes').items() %}
{{ name }}: {{ attribute }}<br>
{% endfor %}
If one is interested in creating own templates, it is a good to start to render the object {{ data }} first, to understand how to parse the object properly.
It is also possible to copy src/core/core/static/presenter_templates/<new-custom-template.txt> to a dynamic folder src/core/taranis_data/presenter_templates so the restart is not necessary.
If needed, templates can be utilized for more complex renderings by leveraging custom attributes.
Currently, this functionality is demonstrated in the text_template.txt file, where the attribute omission of type “Omit Keys” allows for the exclusion of unnecessary attributes from publication. To employ this feature, the administrator simply needs to add this attribute to the relevant report type. Then, within a specific report (Analyze View), they can specify the attributes to omit by listing them as comma-separated strings.
It is essential to ensure that the “Name” used for the report type attribute matches exactly with the key used in the template.
Learn more about what TLP version 2.0 is under first.org/tlp/.
Default value: Clear
Options: Green, Amber, Amber+Strict, Red
All newly collected items by Collectors use this default TLP value. When this setting is changed, it does not affect the items that are already present in Assess section.
This setting can be overridden for each collector with the TLP_LEVEL field.
When a default collector proxy is set, it can then be used in the collectors by enabling the switch USE_GLOBAL_PROXY.
USE_GLOBAL_PROXY is enabled.| # | Per-source proxy | Default proxy | USE_GLOBAL_PROXY | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ❌ | ❌ | false | ⚪ No proxy |
| 2 | ✅ | ❌ | false | 🟢 Per-source proxy |
| 3 | ❌ | ✅ | false | ⚪ No proxy |
| 4 | ✅ | ✅ | false | 🟢 Per-source proxy |
| 5 | ❌ | ❌ | true | ⚪ No proxy |
| 6 | ✅ | ❌ | true | ⚪ No proxy (global forced; default missing) |
| 7 | ❌ | ✅ | true | 🔵 Default proxy |
| 8 | ✅ | ✅ | true | 🔵 Default proxy |
This value is used for REFRESH_INTERVAL for all collectors (OSINT Sources) when this field is left unset individually for all collectors. The syntax is the same as REFRESH_INTERVAL in bot’s settings.
The admin user can access the Taranis API through Swagger UI. Swagger UI displays OpenAPI specifications as an interactive API documentation. Current OpenAPI specifications are available at https://github.com/taranis-ai/taranis-ai/blob/master/src/core/core/static/openapi3_1.yaml
see: Swagger UI
Taranis instance is alive
As an admin, I need to configure OSINT sources to be gathered for intelligence gathering purposes.
As an admin, I need the ability to utilize Word Lists for filtering news items during collection or enhancing them with a Bot. This includes the capability to import and export word lists and apply them based on their designated usage, such as adding tags with the word_list_bot.
As an admin, I need the ability to configure new report types.
As an admin, I need to manage user accounts by creating and deleting users, ensuring they have the necessary access for their tasks.
As an admin, I need to configure Access Control Lists (ACLs) and roles to define permissions for each role. This allows me to effectively manage user permissions, control access to sensitive information, and maintain compliance with organizational policies and regulations.
As an analyst, I require access to a Topics Dashboard feature that displays the most important news topics. This dashboard should prioritize the most frequently occurring tags, offering a snapshot of the prevailing themes and subjects within the collected news items.
As an analsyt, I want to review all stories gathered in a fixed time period. I want to be able to set a stard and end date for items to be displayed. If I set these time limits I want to display Stories with pageing otherwise there will be an infintescroll representing the everchanging nature of stories.
As an analyst, I need the capability to search for news items by entering any text string. To provide a ranked list of results based on the relevance to the search query, enabling me to quickly and effectively identify the most pertinent articles for further analysis.
As an analyst, I want to mark news items as important by voting on them. To allow me to quickly identify and categorize significant articles for easy retrieval at a later time. Each Story includes buttons for down and up voting as well as for marking an story as important. Via a shortcut (ctrl+i) I can mark all selected stories as important.
As an analyst, I want to mark news items as read to prevent myself and other anlyst from viewing the same story multiple times. Each Story contains a button to mark a story as read or unread if already marked as read. The same behaviour can be toggled via a shortcut (ctrl+space).
As an analyst, I need the ability to filter news items based on tags, attributes, or important keywords. To allow me to quickly find relevant news items by applying a tag filter within the tool. The interface should provide an option to enter or select tags, and display the filtered results. In scenarios where no news items match the selected tags, it should result in an empty story list.
As an analyst, I need a feature that enables me to create news items, specifying details such as title, publish date, review, link, article content, and attributes. To maintain data integrity, the editing function will be disabled for any news item once it is included in a report. For ease of use, each news item has an edit button in the Asses view.
As an analyst, I want to create and edit reports directly within the Analyse view. I can create reports from predefined list of report types managed by an administrator. I can edit the metadata of this report, and add Stories to it. I can mark the report as “completed” to allow further processing and publishing.
As an analyst, I require a feature to create reports directly within the Analyse view. I can create reports from predefined list of report types managed by an administrator. I can edit the metadata of this report, and add Stories to it. I can mark the report as “completed” to allow further processing and publishing.
As an analyst, I want to publish the findings of a report. So they can be viewed outside of Taranis AI. I can choose only Reports that match my Product type. I can render a preview of the Product before sharing. I can choose the destination where to publish from a predefined list (publishers) managed by an administrator.
Upon logging in, the analyst is greeted by the Dashboard which prominently displays the most significant tags, offering a quick overview of trending topics and themes. This view sets the context for the analyst’s tasks ahead.
To enhance workflow efficiency, please review the available hotkeys. Additionally, for simplified filtering, set the “End of Shift” time in the user settings. This feature allows the system to display only articles published since the last end of shift, ensuring you see content that hasn’t been reviewed yet.
To assess your items, go to the Assess section and set the time filter. Apply the “not read” and “not important” filters. Mark as read any items that have been read but are considered unimportant. Continue working through these items until all are marked as read, focusing only on checking summaries.
Next, set the filter to “not read” and “important”. Verify the importance of each item and mark it as read if not important. Check whether the item is part of an older report and determine if it still adds value. If not, remove the “important” tag and mark the item as read. If multiple items discuss the same topic, merge them.
To update a summary manually or with AI, first click the “Edit Story” button. Then, you can either edit the summary yourself or use the “Summarize with AI” for a quicker option. Send important or sector-specific items via email. Optionally, you can upvote or downvote items and add them to the relevant reports.
Finally, remove the “important” tag and mark the item as read. For greater efficiency, consider using the time filter to focus on the most recent content.
During the review process in the Assess tab, the analyst has several tools at their disposal to optimize their workflow:
Voting on Stories: The analyst can vote stories up or down and mark them as important using buttons or the shortcut (Ctrl+I). This helps highlight stories of particular relevance.
Mark as Read: To maintain efficiency and avoid redundancy, the analyst can mark stories as read or unread using a button or the shortcut (Ctrl+Space).
Tags: Tag filters can be applied to narrow down the selection to the most relevant articles, improving focus. If a story needs editing or creation, the analyst can do so directly within the Assess tab, where news items can be adjusted until they are locked into a report. This ensures the content remains fresh and accurate.
Once all relevant stories are collected and reviewed, the analyst moves to the Analyze tab to finalize the report and mark it as completed. This step transitions the process from review to dissemination
To analyze your items, go to the Analyze section and review them as done in Assess by merging and removing items. Ensure everything is ready for a final review. Add news items to the appropriate categories, save, and mark the process as completed.
Finally, the Publish tab is where the compiled report transforms into a product ready for external consumption. The analyst chooses a product type that fits the report, reviews the final product via a rendered preview, and selects a publication destination from a managed list. This final step disseminates the insights gathered and analyzed, extending the impact of the analyst’s work beyond the confines of Taranis AI.
See https://github.com/taranis-ai/.github/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md